
Breaking News
 Dale Whitaker on conservative media's role in gold scams
Dale Whitaker on conservative media's role in gold scams
 Cucumber and celery juices: Decoding the hydration and health benefits
Cucumber and celery juices: Decoding the hydration and health benefits
 LAWYER: If the City Demands a MANDATORY 'Home Inspection,' DO THIS.
LAWYER: If the City Demands a MANDATORY 'Home Inspection,' DO THIS.
Top Tech News
 NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
NASA announces strongest evidence yet for ancient life on Mars
 Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
Caltech has successfully demonstrated wireless energy transfer...
 The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
The TZLA Plasma Files: The Secret Health Sovereignty Tech That Uncle Trump And The CIA Tried To Bury
 Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
Nano Nuclear Enters The Asian Market
 Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
 World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
 New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
 Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
 Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
 Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
Improved Desalination Technology is Quenching the World's Thirst
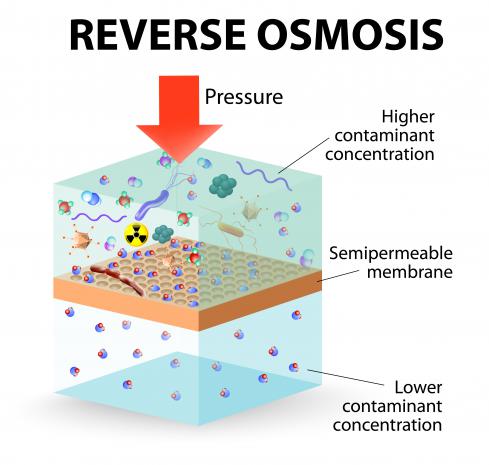
Worldwide, some 700 million people don't have access to clean water. According to the United Nations, this figure will rise to roughly 1.8 billion within the next 10 years. To prepare for a growing population and the imminent shortage of fresh, potable water, scientists have found efficient means of warding off this epidemic by drinking…seawater. The process is called desalination, and it's a technology that, at the risk of sounding hyperbolic, could be key to ensuring a better future for the human race.
Desalination is surprisingly simple. Through the process of seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO), desalination filters salt from seawater to produce fresh, drinkable water. By applying pressure, saline water is forced through a semipermeable membrane–basically very thin plastic sheets with tiny holes in it. In reverse osmosis, the membrane pores are incredibly small, only about 200 nanometers thick, allowing water molecules to squeeze past, but not salt. To put in perspective–a human hair is around 75,000 nanometers in diameter.

 55D Compliance Chess?
55D Compliance Chess?

