
Breaking News
 Christmas Truce of 1914, World War I - For Sharing, For Peace
Christmas Truce of 1914, World War I - For Sharing, For Peace
 The Roots of Collectivist Thinking
The Roots of Collectivist Thinking
 What Would Happen if a Major Bank Collapsed Tomorrow?
What Would Happen if a Major Bank Collapsed Tomorrow?
Top Tech News
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
 A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
 Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
IBM Creates A Molecule That Could Destroy All Viruses
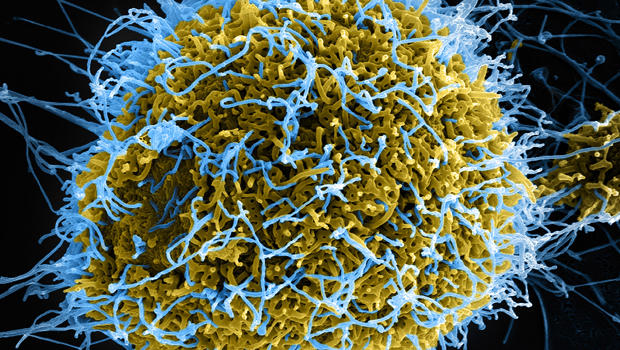
Finding a cure for viruses like Ebola, Zika, or even the flu is a challenging task. Viruses are vastly different from one another, and even the same strain of a virus can mutate and change--that's why doctors give out a different flu vaccine each year. But a group of researchers at IBM and the Institute of Bioengineering and Nanotechnology in Singapore sought to understand what makes all viruses alike. Using that knowledge, they've come up with a macromolecule that may have the potential to treat multiple types of viruses and prevent them from infecting us. The work was published recently in the journal Macromolecules.
For their study, the researchers ignored the viruses' RNA and DNA, which could be key areas to target, but because they change from virus to virus and also mutate, it's very difficult to target them successfully.

 The State's Last Stand
The State's Last Stand


