
Breaking News
 BREAKING: CBS 60 Minutes: revealed a previously unknown weapon that they believe is linked...
BREAKING: CBS 60 Minutes: revealed a previously unknown weapon that they believe is linked...
 The Year of Adam Smith: Why the Savvy Scotsman Remains So Important
The Year of Adam Smith: Why the Savvy Scotsman Remains So Important
 Trump sons trigger 'corruption' uproar as Pentagon drone venture surfaces amid Iran war
Trump sons trigger 'corruption' uproar as Pentagon drone venture surfaces amid Iran war
 Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
Will the Dollar be a Casualty of the Iran War?
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Embedded nanoparticles clear the way for smart glass devices
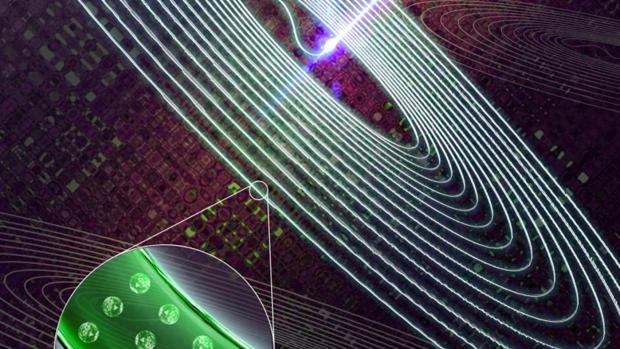
Able to be molded in almost any shape, and even extruded into optical fibers, the researchers claim that this new "hybrid glass" could be used to create new smart glass devices, including smart 3D displays and remote radiation sensors.
Australian researchers at the University of Adelaide, in collaboration with Macquarie University and the University of Melbourne, created this glowing glass by molding upconversion luminescent nanoparticles directly into the translucent material using a two-temperature glass-melting technique. The embedded nanoparticles produce luminescence when two or more low-energy, longer wavelength (usually infrared) photons are absorbed by the particles which then emit a single higher-energy, shorter wavelength photon in return.
"These novel luminescent nanoparticles, called upconversion nanoparticles, have become promising candidates for a whole variety of ultra-high tech applications such as biological sensing, biomedical imaging and 3D volumetric displays," says Dr Tim Zhao, from the University of Adelaide's School of Physical Sciences and Institute for Photonics and Advanced Sensing (IPAS). "Integrating these nanoparticles into glass, which is usually inert, opens up exciting possibilities for new hybrid materials and devices that can take advantage of the properties of nanoparticles in ways we haven't been able to do before."



