
Breaking News
 BANK OF AMERICA SURRENDERS: BofA Just Issued a $309 Silver Alert (Physical Premiums Exploding)
BANK OF AMERICA SURRENDERS: BofA Just Issued a $309 Silver Alert (Physical Premiums Exploding)
 Steve Witkoff says they are close to finishing "a prosperity agreement" for Ukraine,...
Steve Witkoff says they are close to finishing "a prosperity agreement" for Ukraine,...
 NOW - Starmer says a declaration of intent has been signed...
NOW - Starmer says a declaration of intent has been signed...
 Remarks at the New Jersey Bankers Association, Jersey City, New Jersey
Remarks at the New Jersey Bankers Association, Jersey City, New Jersey
Top Tech News
 The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
 See inside the tech-topia cities billionaires are betting big on developing...
See inside the tech-topia cities billionaires are betting big on developing...
 Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
 Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Regenerating connections between eye and brain restores vision in mice
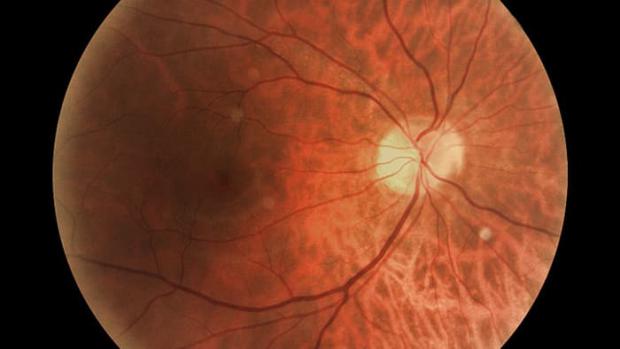
Eyes are complex machines, and visual processing of the images they take in accounts for more than a third of brain functioning. It starts with photoreceptor cells at the back of the retina that react to light wavelengths and send their electrically-coded data to the 30 or so types of retinal ganglion cells, each one specializing in processing specific aspects of vision; they're also the only nerve cells connecting the eye with the brain.
Projected from the ganglion cells are long, slender projections called axons, which are bundled together along the optic nerve from the eye before fanning out to various regions in the brain where the visual input is interpreted. Unfortunately, axons in the brain or spinal cord don't regenerate on their own once they've been damaged, leading to permanent vision loss. One reason for this is the reduction over time of a cascade of growth-enhancing molecular interactions within axon cells known as the mTOR pathway.
The condition of the mice's eyes in the study was similar to glaucoma, which is associated with pressure on the optic nerve to the point where damage occurs. Affecting nearly 70 million people globally, glaucoma and is the second-leading cause of blindness after cataracts, and currently there's no cure. Injuries, retinal detachment, and some tumors and brain cancers can also damage the optic nerve.



