
Breaking News
 Quantum walkie-talkie: China tests world's first GPS-free radio for border zones
Quantum walkie-talkie: China tests world's first GPS-free radio for border zones
 RIGHT NOW!: Why was lawyer Van Kessel, of the civil case on the merits in the Netherlands, arrested?
RIGHT NOW!: Why was lawyer Van Kessel, of the civil case on the merits in the Netherlands, arrested?
 PENSION FUNDS PANIC BUYING SILVER - Ratio Below 60 Triggers $50B Wave (Danger Next Week)
PENSION FUNDS PANIC BUYING SILVER - Ratio Below 60 Triggers $50B Wave (Danger Next Week)
 Dollar set for worst year since 2017, yen still in focus
Dollar set for worst year since 2017, yen still in focus
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Stem cells coaxed into regenerating bone while leaving tumors out
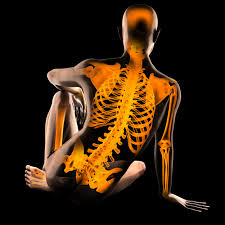
With successful animal tests already in the bag, the findings could have a big impact on the treatment of bone defects, and for healing traumatic bone injuries.
Pluripotent stem cells are extremely versatile, with the capability of becoming any type of cell found in the body, a process known as differentiation. In 2012, a Johns Hopkins study saw the development of a technique to regress blood cells into pluripotent stem cells, and over the years we've seen them used to create functional intestinal tissue, grow human retinas, and much more.
Despite past successes in utilizing the versatile stem cells, coaxing them to develop into a particular type of cell is anything but simple. The UC San Diego team describes the process as being akin to following a very complex recipe, with a long list of ingredients and a complex set of steps.



