
Breaking News
 IT'S OVER: Banks Tap Fed for $17 BILLION as Silver Shorts Implode
IT'S OVER: Banks Tap Fed for $17 BILLION as Silver Shorts Implode
SEMI-NEWS/SEMI-SATIRE: December 28, 2025 Edition
 China Will Close the Semiconductor Gap After EUV Lithography Breakthrough
China Will Close the Semiconductor Gap After EUV Lithography Breakthrough
 The Five Big Lies of Vaccinology
The Five Big Lies of Vaccinology
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Scar-free wound healing could be on its way
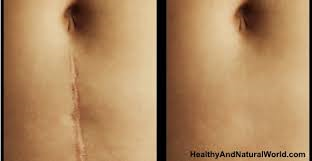
Recently, though, scientists from the University of Pennsylvania and the University of California, Irvine succeeded in addressing both factors. They're now able to get wounds to heal with regenerated skin, instead of with scar tissue.
Myofibroblasts are the most common type of cell found in healing wounds, and they're associated with scar formation. Led by U Penn's Dr. George Cotsarelis, the research team was able to get those cells to transform into ones known as adipocytes – these are the fat cells that are present in normal skin, but absent in scars.
Scientists in the Cotsarelis Lab already knew which growth factors were necessary for hair follicles to form in the skin. This knowledge previously allowed them to induce follicles to grow at wound sites on mice, although that would supposedly only be solving half of the problem.



