
Breaking News
 Tucker Exposes Trump Would-Be Assassin Thomas Crooks' Social Media History, The FBI Coverup...
Tucker Exposes Trump Would-Be Assassin Thomas Crooks' Social Media History, The FBI Coverup...
 This Was A Major Red Flag In 2008, And Now It Is Happening Again!
This Was A Major Red Flag In 2008, And Now It Is Happening Again!
 Trump orders DOJ probe into Epstein's alleged ties with JPMorgan, Clinton and other Democrats
Trump orders DOJ probe into Epstein's alleged ties with JPMorgan, Clinton and other Democrats
Top Tech News
 Blue Origin New Glenn 2 Next Launch and How Many Launches in 2026 and 2027
Blue Origin New Glenn 2 Next Launch and How Many Launches in 2026 and 2027
 China's thorium reactor aims to fuse power and parity
China's thorium reactor aims to fuse power and parity
 Ancient way to create penicillin, a medicine from ancient era
Ancient way to create penicillin, a medicine from ancient era
 Goodbye, Cavities? Scientists Just Found a Way to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Goodbye, Cavities? Scientists Just Found a Way to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Scientists Say They've Figured Out How to Transcribe Your Thoughts From an MRI Scan
Scientists Say They've Figured Out How to Transcribe Your Thoughts From an MRI Scan
 SanDisk stuffed 1 TB of storage into the smallest Type-C thumb drive ever
SanDisk stuffed 1 TB of storage into the smallest Type-C thumb drive ever
 Calling Dr. Grok. Can AI Do Better than Your Primary Physician?
Calling Dr. Grok. Can AI Do Better than Your Primary Physician?
 HUGE 32kWh LiFePO4 DIY Battery w/ 628Ah Cells! 90 Minute Build
HUGE 32kWh LiFePO4 DIY Battery w/ 628Ah Cells! 90 Minute Build
 What Has Bitcoin Become 17 Years After Satoshi Nakamoto Published The Whitepaper?
What Has Bitcoin Become 17 Years After Satoshi Nakamoto Published The Whitepaper?
Fat can be used to Help Wounds Heal Without Scars, skin regeneration and not scarring
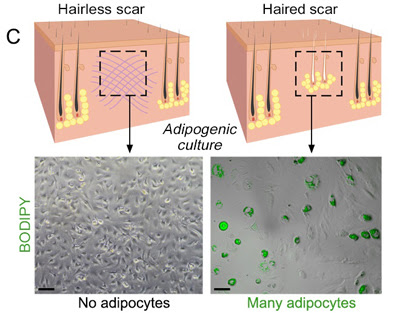
The method involves transforming the most common type of cells found in wounds into fat cells – something that was previously thought to be impossible in humans. Researchers began this work at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, which led to a large-scale, multi-year study in connection with the Plikus Laboratory for Developmental and Regenerative Biology at the University of California, Irvine. They published their findings online in the journal Science on Thursday, January 5th, 2017.
Fat cells called adipocytes are normally found in the skin, but they're lost when wounds heal as scars. The most common cells found in healing wounds are myofibroblasts, which were thought to only form a scar. Scar tissue also does not have any hair follicles associated with it, which is another factor that gives it an abnormal appearance from the rest of the skin. Researchers used these characteristics as the basis for their work – changing the already present myofibroblasts into fat cells that do not cause scarring.
"Essentially, we can manipulate wound healing so that it leads to skin regeneration rather than scarring," said George Cotsarelis, MD, the chair of the Department of Dermatology and the Milton Bixler Hartzell Professor of Dermatology at Penn, and the principal investigator of the project. "The secret is to regenerate hair follicles first. After that, the fat will regenerate in response to the signals from those follicles."

 A WORLD OF DEBT
A WORLD OF DEBT
 Unbanked In A Connected World
Unbanked In A Connected World

