
Breaking News
 Ron Paul's Warnings Have Come True: Rising Debt, Endless War & Economic Collapse
Ron Paul's Warnings Have Come True: Rising Debt, Endless War & Economic Collapse
 LICENSE TO FARM | Great Britain's Quiet Shift to Conditional Agriculture.
LICENSE TO FARM | Great Britain's Quiet Shift to Conditional Agriculture.
 Why the Classic Computer Science Degree Might Leave You Jobless in 2026 - And What to Do Instead
Why the Classic Computer Science Degree Might Leave You Jobless in 2026 - And What to Do Instead
 Pentagon To Send 200 Troops to Nigeria
Pentagon To Send 200 Troops to Nigeria
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
The brain uses REM sleep to cut unneeded connections
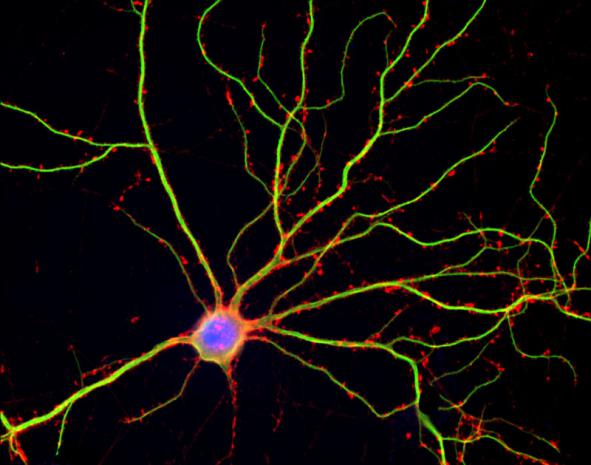
REM sleep is known to help solidify memories, but the mechanism for making memories more permanent is not well-understood. A recent study published in Nature Neuroscience shows that, during REM sleep, some of the structures neurons use to make connections with each other are pruned, while others are maintained and strengthened. The findings indicate that sleep's role in solidifying memories comes through allowing the brain time to selectively eliminate or maintain newly formed neural connections.
Dendritic spines are small outgrowths on a neuron's dendrite, which is the portion of the neuron that receives chemical signals from other neurons. These spines enhance the strength of connections between neurons so they can play an important role in strengthening new neural circuits and solidifying new memories. These spines aren't permanent structures; instead, nerve cells can create new ones or get rid of existing ones (a process called pruning) as the importance of different connections shifts.
The new memories in this case were formed in mice, which were trained to complete a treadmill-like motor task. Then, the mice were either deprived of REM sleep or allowed to experience this form of sleep. The mice that were allowed REM showed significantly higher pruning of new dendritic spines compared to the mice that were REM sleep deprived. This difference in pruning was only seen for new dendritic spines, and previously existing dendritic spines were pruned at the same rate.



