Breaking News
 Quantum walkie-talkie: China tests world's first GPS-free radio for border zones
Quantum walkie-talkie: China tests world's first GPS-free radio for border zones
 RIGHT NOW!: Why was lawyer Van Kessel, of the civil case on the merits in the Netherlands, arrested?
RIGHT NOW!: Why was lawyer Van Kessel, of the civil case on the merits in the Netherlands, arrested?
 PENSION FUNDS PANIC BUYING SILVER – Ratio Below 60 Triggers $50B Wave (Danger Next Week)
PENSION FUNDS PANIC BUYING SILVER – Ratio Below 60 Triggers $50B Wave (Danger Next Week)
 Dollar set for worst year since 2017, yen still in focus
Dollar set for worst year since 2017, yen still in focus
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
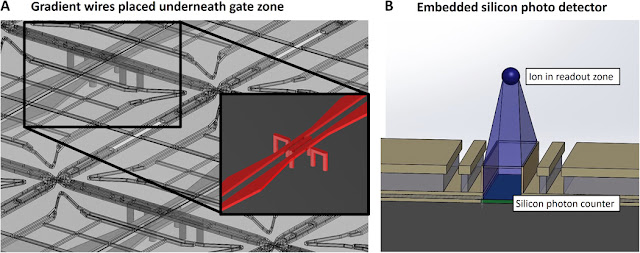
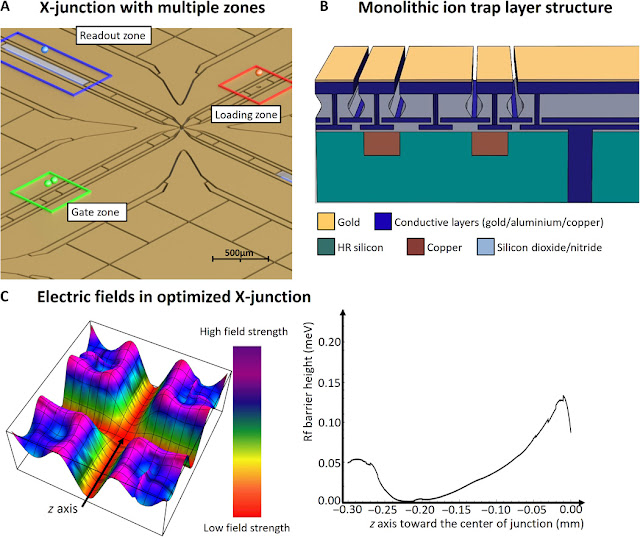
Large scale microwave trapped ion universal quantum computer design ...

The microwave trapped ion universal quantum computer design work features a new invention permitting actual quantum bits to be transmitted between. individual quantum computing modules in order to obtain a fully modular large-scale machine capable of reaching nearly arbitrary large computational processing powers.
Previously, scientists had proposed using fibre optic connections to connect individual computer modules. The new invention introduces connections created by electric fields that allow charged atoms (ions) to be transported from one module to another. This new approach allows 100,000 times faster connection speeds between individual quantum computing modules compared to current state-of-the-art fibre link technology.
The new blueprint is the work of an international team of scientists from the University of Sussex (UK), Google (USA), Aarhus University (Denmark), RIKEN (Japan) and Siegen University (Germany).
They estimate that a 2 billion trapped ion system could be used to crack 2048 bit encryption in 110 days. In December 2009, Lenstra and his team announced the factorization of a 768-bit RSA modulus.
In 2012, a 923 bit code was cracked using 21 computers
The Lenstra group estimated that factoring a 1024-bit RSA modulus would be about 1,000 times harder than their record effort with the 768-bit modulus, or in other words, on the same hardware, with the same conditions, it would take about 1,000 times as long. They also estimated that their record achievement would have taken 1,500 years if they normalized processing power to that of the standard desktop machine at the time - this assumption is based on a 2.2 Ghz AMD Opteron processor with 2GB RAM. Breaking a DigiCert 2048-bit SSL certificate would take about 4.3 billion times longer (using the same standard desktop processing) than doing it for a 1024-bit key. It is therefore estimated, that standard desktop computing power would take 4,294,967,296 x 1.5 million years to break a DigiCert 2048-bit SSL certificate. Or, in other words, a little over 6.4 quadrillion years.
As a next step, the team will construct a prototype quantum computer, based on this design, at the University.