
Breaking News
 IT'S OVER: Banks Tap Fed for $17 BILLION as Silver Shorts Implode
IT'S OVER: Banks Tap Fed for $17 BILLION as Silver Shorts Implode
SEMI-NEWS/SEMI-SATIRE: December 28, 2025 Edition
 China Will Close the Semiconductor Gap After EUV Lithography Breakthrough
China Will Close the Semiconductor Gap After EUV Lithography Breakthrough
 The Five Big Lies of Vaccinology
The Five Big Lies of Vaccinology
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
1,000 times more efficient nano-LED opens door to faster microchip
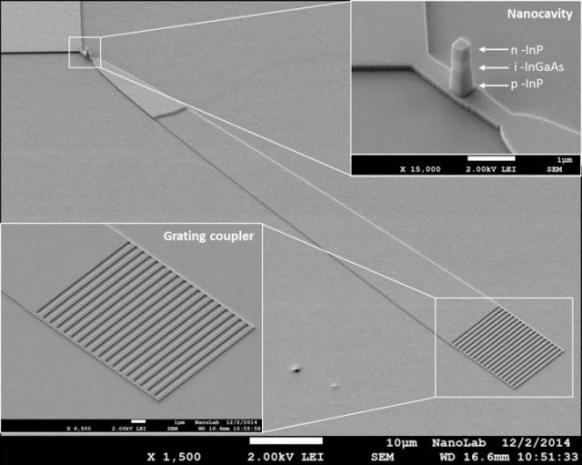
Optical connections are the obvious successors but optical data transmission requires an adequate nanoscale light source, and this has been lacking. Scientists at Eindhoven University of Technology (TU/e) now have created a light source that has the right characteristics: a nano-LED that is 1000 times more efficient than its predecessors, and is capable of handling gigabits per second data speeds. They have published their findings in the online journal Nature Communications.
With electrical cables reaching their limits, optical connections like fiberglass are increasingly becoming the standard for data traffic. Over longer distances almost all data transmission is optical. Within computer systems and microchips, too, the growth of data traffic is exponential, but that traffic is still electronic, and this is increasingly becoming a bottleneck. Since these connections ('interconnects') account for the majority of the energy consumed by chips, many scientists around the world are working on enabling optical (photonic) interconnects. Crucial to this is the light source that converts the data into light signals which must be small enough to fit into the microscopic structures of microchips. At the same time, the output capacity and efficiency have to be good. Especially the efficiency is a challenge, as small light sources, powered by nano- or microwatts, have always performed very inefficiently to date.



