
Breaking News
 The Coming Storm: A wake-up call for the prepared mind
The Coming Storm: A wake-up call for the prepared mind
 Europe Is Building a Digital Identity System for 450 Million People
Europe Is Building a Digital Identity System for 450 Million People
 I've Never Made Something Like This Before - Because Staying Silent Isn't an Option
I've Never Made Something Like This Before - Because Staying Silent Isn't an Option
 Putin DECLARES the EU is the only party that wants to continue the War:
Putin DECLARES the EU is the only party that wants to continue the War:
Top Tech News
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
 The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
 US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
 Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
 CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
Robotic prosthetic taps spinal nerve signals
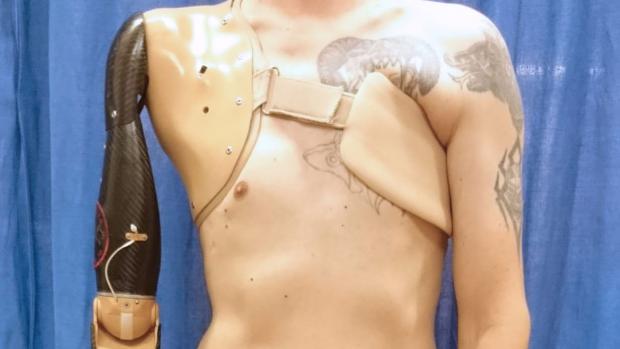
Could a new robotic prosthetic arm that detects signals from spinal nerve cells nudge researchers closer to creating an artificial limb that resembles the real thing?
The problem with muscle-controlled robotic arms is that they rely on twitches from amputated limbs, the fibers of which are often damaged.
"When an arm is amputated the nerve fibres and muscles are also severed, which means that it is very difficult to get meaningful signals from them to operate a prosthetic," explains Dario Farina, a professor of bioengineering at Imperial College London.
This limits the number of tasks the artificial limb can perform and explains why up to 50 percent of users end up dumping them in frustration, he claims. But what if the prosthetic made use of the nervous system instead, so that the signals sent from the motor neurons, which control muscle movement, could be deciphered more clearly? Could this lead to the development of more intuitive robotic arms? This is what Farina and his team wanted to find out.

 Renewable Water From Air.
Renewable Water From Air.

