
Breaking News
 China Will Close the Semiconductor Gap After EUV Lithography Breakthrough
China Will Close the Semiconductor Gap After EUV Lithography Breakthrough
 The Five Big Lies of Vaccinology
The Five Big Lies of Vaccinology
 Large global study analyzing data from 192 countries has sparked intense debate by suggesting...
Large global study analyzing data from 192 countries has sparked intense debate by suggesting...
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
This robot is perfectly designed to drill tiny tunnels in your skull
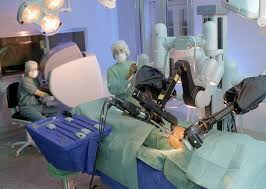
Imagine rolling into an operating room to find that your surgical team included a robot. While full-fledged robotic surgeons aren't quite ready for the spotlight, automatons have already found a foothold in the surgical theater. Some systems allow doctors to control robotic instruments—ones able to slice and dice with inhuman precision—using controls or a computer screen, while other medical robots take a doctor's place entirely to conduct specific segments of a larger surgery. Now scientists have taken a big step forward with the latter type of bot: in a study published Wednesday in Science Robotics, a team reports the first ever robot-assisted cochlear implantation surgery.
"We were on this project for more than eight years," says lead study author Stefan Weber, a professor at the University of Bern, Switzerland's ARTORG Center for Biomedical Engineering Research. "And in contrast to a lot of research, we really stuck to one application for the entire time."

 This is why RAM costs so much
This is why RAM costs so much

