
Breaking News
 Canada's MAID CULTURE OF DEATH Just Hit Rock Bottom: KILLING PRISONERS NOW!!!
Canada's MAID CULTURE OF DEATH Just Hit Rock Bottom: KILLING PRISONERS NOW!!!
 Weight gain single-handedly prevented by a gut microbe
Weight gain single-handedly prevented by a gut microbe
 Doug Casey on 2025's Defining Events and What Comes Next
Doug Casey on 2025's Defining Events and What Comes Next
 BREAKING: Officer Tatum & Other Investigators Believe A Potential Suspect In The Brown...
BREAKING: Officer Tatum & Other Investigators Believe A Potential Suspect In The Brown...
Top Tech News
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
 A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
 Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
 Advanced Propulsion Resources Part 1 of 2
Advanced Propulsion Resources Part 1 of 2
 PulsarFusion a forward-thinking UK aerospace company, is pushing the boundaries of space travel...
PulsarFusion a forward-thinking UK aerospace company, is pushing the boundaries of space travel...
 Dinky little laser box throws big-screen entertainment from inches away
Dinky little laser box throws big-screen entertainment from inches away
 'World's first' sodium-ion flashlight shines bright even at -40 ºF
'World's first' sodium-ion flashlight shines bright even at -40 ºF
Nanowire retinal implant could restore sight with better resolution
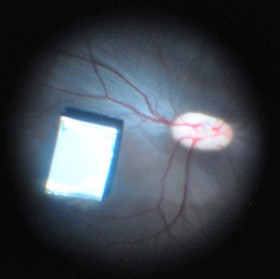
Now engineers have tested a new nano-scale system that could be implanted onto a patient's retina to respond to light by directly stimulating the neurons that send visual signals to the brain. Unlike other systems, the new device wouldn't require any external sensors, and can provide a much higher resolution.
Two of the most promising bionic eyes in development are the Argus II, built by Second Sight, and a similar system created by researchers at Bionic Vision Australia. Both of these prosthetics involve first implanting electrodes into the eye, then connecting them to external sensors that can be worn like glasses. Light signals from these camera-like sensors are translated into electrical impulses and sent to the implants to stimulate the neurons at the retina, which in turn send the visual information to the brain by way of the optic nerve.



