
Breaking News
 Iran war escalates in all the wrong directions
Iran war escalates in all the wrong directions
 US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
 Full Alex Jones Show: Trump Is Preparing To Send US Special Forces Into Iran...
Full Alex Jones Show: Trump Is Preparing To Send US Special Forces Into Iran...
 We Are Persian, Not Iranian: The Diaspora's Response to the Fall of the Islamic Republic
We Are Persian, Not Iranian: The Diaspora's Response to the Fall of the Islamic Republic
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
This New Graphene-Based Electrode Could Boost Solar Storage by 3,000%
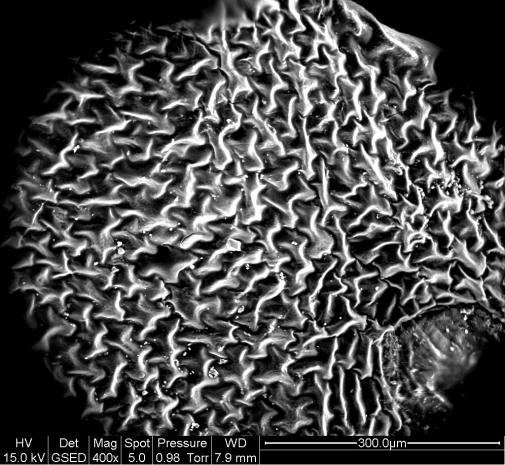
Drawing inspiration from the plant world, researchers have invented a new electrode that could boost our current solar energy storage by an astonishing 3,000 percent.
The technology is flexible and can be attached directly to solar cells - which means we could finally be one step closer to smartphones and laptops that draw their power from the Sun, and never run out.
A major problem with reliably using solar energy as a power source is finding an efficient way to store it for later use without leakage over time.
For that purpose, engineers have been turning to supercapacitors - a type of technology that can charge extremely fast and release energy in large bursts. But for now, supercapacitors aren't able to store enough energy to make them viable as solar batteries.
So a team from RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia decided to investigate how living organisms manage to cram a lot of energy into a small space, and their imagination was soon spurred on by the ingenious fractal-based leaves of a common North American plant - the western swordfern (Polystichum munitum).



