
Breaking News
 Iran (So Far Away) - Official Music Video
Iran (So Far Away) - Official Music Video
 COMEX Silver: 21 Days Until 429 Million Ounces of Demand Meets 103 Million Supply. (March Crisis)
COMEX Silver: 21 Days Until 429 Million Ounces of Demand Meets 103 Million Supply. (March Crisis)
 Marjorie Taylor Greene: MAGA Was "All a Lie," "Isn't Really About America or the
Marjorie Taylor Greene: MAGA Was "All a Lie," "Isn't Really About America or the
 Why America's Two-Party System Will Never Threaten the True Political Elites
Why America's Two-Party System Will Never Threaten the True Political Elites
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
3D printing of glass with precision of tens of microns
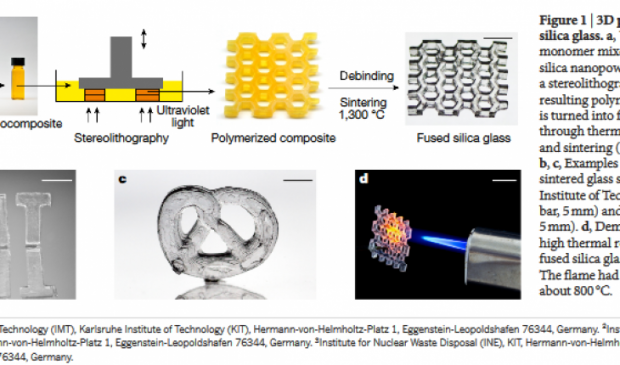
As a consequence of the properties of glass, such as transparency, thermal stability and resistance to acids, the use of this material in 3D-printing opens up manifold new applications in production and research, such as optics, data transmission, and biotechnology.
The scientists mix nanoparticles of high-purity quartz glass and a small quantity of liquid polymer and allow this mixture to be cured by light at specific points – by means of stereolithog-raphy. The material, which has remained liquid, is washed out in a solvent bath, leaving only the desired cured structure. The polymer still mixed in this glass structure is subsequently removed by heat-ing.
"The shape initially resembles that of a pound cake; it is still unstable, and therefore the glass is sintered in a final step, i.e. heated so that the glass particles are fused," explains Rapp.



