
Breaking News
 300 WSM Ballistics Tables From Common Ammo Makers
300 WSM Ballistics Tables From Common Ammo Makers
 Oil Tankers Turning Off Transponders – 10% of Regular Volume in Dark Fleet Made Hormuz Passage
Oil Tankers Turning Off Transponders – 10% of Regular Volume in Dark Fleet Made Hormuz Passage
 Meet DARPA's X-76: The rotorcraft that flies like a jet
Meet DARPA's X-76: The rotorcraft that flies like a jet
 You've Been LIED to About Healthy Eating: The Truth Could Add Decades to Your Life
You've Been LIED to About Healthy Eating: The Truth Could Add Decades to Your Life
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Fiber-reinforced hydrogel is 5 times stronger than steel
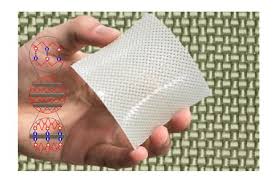
Hydrogels have shown significant potential in everything from wound dressings to soft robots, but their applications have been limited from their lack of toughness – until now. A team of scientists at Hokkaido University have developed a new set of hydrogel composites or "fiber-reinforced soft composites" that combine hydrogels with woven fiber fabric to create a material that is five times stronger than carbon steel.
Composite materials have been around for millennia and the principle is very simple. A very soft substance like mud can be made strong enough to make bricks by adding straw as a tempering material. The same applies to adding crushed pottery to brick, seashells fragments to ceramic, or glass fiber to plastic.
The latter is very similar to the fiber-reinforced hydrogel. Hydrogels are made of hydrophilic polymer chains that absorb up to 90 percent water. They aren't very strong or durable, but by adding glass tiny fibers the researchers created a tough, bendable, stretchable material.
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) images of the fiber-reinforced hydrogels (Credit: Hokkaido University)




