
Breaking News
6.5x55 Swedish vs. 6.5 Creedmoor: The New 6.5mm Hotness
Best 7mm PRC Ammo: Hunting and Long-Distance Target Shooting
 Christmas Truce of 1914, World War I - For Sharing, For Peace
Christmas Truce of 1914, World War I - For Sharing, For Peace
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Claimed antiaging benefits of blood transfusion from teenagers to those over 35
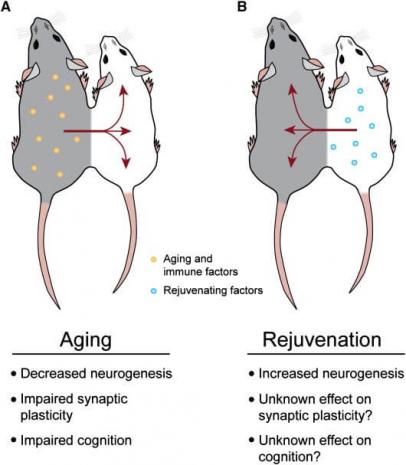
Blood biomarkers
None of the people in the study had cancer at the time of treatment, however Karmazin's team looked at the levels of certain proteins called carcinoembryonic antigens. These chemicals are found in the blood of healthy people at low concentrations, but in larger amounts these antigens can be a sign of having cancer.
The team detected that the levels of carcinoembryonic antigens fell by around 20 per cent in the blood of people who received the treatment. However, there was no control group or placebo treatment in the study, and it isn't clear whether a 20 per cent reduction in these proteins is likely to affect someone's chances of developing cancer.
Karmazin says the team also saw a 10 per cent fall in blood cholesterol levels. "That was a surprise," he says. This may help explain why a study by a different company last year found that heart health improved in old mice that were given blood from human teenagers.

 The State's Last Stand
The State's Last Stand


