
Breaking News
 Charlie's Killer Was MKUltra'd?
Charlie's Killer Was MKUltra'd?
 Doctors are finally admitting that biopsies Spread Cancer…
Doctors are finally admitting that biopsies Spread Cancer…
 We MUST keep talking about this, demand Voter ID. Joe Rogan and Elon Musk on Fraud
We MUST keep talking about this, demand Voter ID. Joe Rogan and Elon Musk on Fraud
 Nick Shirley exposes there are 1,200 medical transport companies in Minnesota.
Nick Shirley exposes there are 1,200 medical transport companies in Minnesota.
Top Tech News
 The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
 See inside the tech-topia cities billionaires are betting big on developing...
See inside the tech-topia cities billionaires are betting big on developing...
 Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
 Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Vitamin D – a new sunburn treatment?
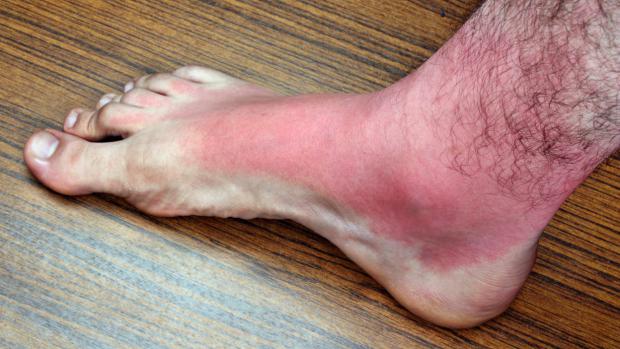
The double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial started by giving 20 test subjects a small UV-lamp-delivered sunburn on their inner arm. Within one hour, they were then given either a placebo pill, or 50,000, 100,000, or 200,000 IU of vitamin D. Their skin was subsequently analyzed 24, 48, 72 hours and one week after the experiment.
While the placebo and the lower doses had little to no effect, the higher doses significantly reduced inflammation and redness, plus the test subjects experienced a jump in gene activity related to skin barrier repair. The scientists believe this was because vitamin D increases levels of an enzyme known as arginase-1, which both boosts tissue repair and activates anti-inflammatory proteins.
That said, the effective doses in the experiment were far above the 400-IU daily recommended allowance of vitamin D.
"I would not recommend at this moment that people start taking vitamin D after sunburn based on this study alone," says lead scientist Dr. Kurt Lu. "But, the results are promising and worthy of further study."



