
Breaking News
 Pentagon To Send 200 Troops to Nigeria
Pentagon To Send 200 Troops to Nigeria
 Trump Says He May Send Second Aircraft Carrier to Middle East To Prepare for Potential Attack...
Trump Says He May Send Second Aircraft Carrier to Middle East To Prepare for Potential Attack...
 A Market Crash and Recession Are Bullish, Not Bearish
A Market Crash and Recession Are Bullish, Not Bearish
 What Are They Still Hiding? New Epstein Questions Point to a Much Bigger Cover-Up
What Are They Still Hiding? New Epstein Questions Point to a Much Bigger Cover-Up
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
New propulsion system gets CubeSats moving with teaspoons of water
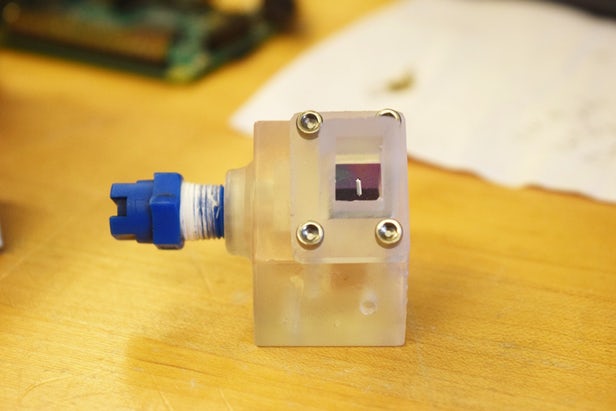
Now, to make CubeSats more maneuverable, a team from Purdue University has developed a system that would allow the mini satellites to safely propel themselves by spraying jets of ordinary water.
The Purdue prototype was a CubeSat measuring 10 cm3 (0.6 in3) and weighing 2.8 kg (6 lb), loaded with off-the-shelf electronic components normally used for Internet of Things devices. There's a computer that wirelessly receives instructions and relays them to an inertial measurement unit that works out how to act on them. But the star of the show was the propulsion system, dubbed a Film-Evaporation MEMS Tunable Array (FEMTA) thruster.
Four of these FEMTA thrusters were built into the prototype, each one carrying about a teaspoon of ultra-purified water. The tank is full of capillaries about 10 microns wide, which is too small for the water to flow out thanks to its surface tension. To control when it escapes, small heaters around the edges of these holes can be activated on demand, warming the water into vapor and creating tiny blasts that turn the craft.



