
Breaking News
 Verizon to Slash 15 Percent of Its Workforce, About 15,000 Jobs
Verizon to Slash 15 Percent of Its Workforce, About 15,000 Jobs
 The SCARY SHIFT from SCARCITY to ABUNDANCE
The SCARY SHIFT from SCARCITY to ABUNDANCE
 Foreclosure surge signals housing market distress as costs spiral out of control
Foreclosure surge signals housing market distress as costs spiral out of control
 Nearly 1,000 flights canceled despite government reopening, disruptions expected for days
Nearly 1,000 flights canceled despite government reopening, disruptions expected for days
Top Tech News
 Blue Origin New Glenn 2 Next Launch and How Many Launches in 2026 and 2027
Blue Origin New Glenn 2 Next Launch and How Many Launches in 2026 and 2027
 China's thorium reactor aims to fuse power and parity
China's thorium reactor aims to fuse power and parity
 Ancient way to create penicillin, a medicine from ancient era
Ancient way to create penicillin, a medicine from ancient era
 Goodbye, Cavities? Scientists Just Found a Way to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Goodbye, Cavities? Scientists Just Found a Way to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Scientists Say They've Figured Out How to Transcribe Your Thoughts From an MRI Scan
Scientists Say They've Figured Out How to Transcribe Your Thoughts From an MRI Scan
 SanDisk stuffed 1 TB of storage into the smallest Type-C thumb drive ever
SanDisk stuffed 1 TB of storage into the smallest Type-C thumb drive ever
 Calling Dr. Grok. Can AI Do Better than Your Primary Physician?
Calling Dr. Grok. Can AI Do Better than Your Primary Physician?
 HUGE 32kWh LiFePO4 DIY Battery w/ 628Ah Cells! 90 Minute Build
HUGE 32kWh LiFePO4 DIY Battery w/ 628Ah Cells! 90 Minute Build
 What Has Bitcoin Become 17 Years After Satoshi Nakamoto Published The Whitepaper?
What Has Bitcoin Become 17 Years After Satoshi Nakamoto Published The Whitepaper?
The protein that can make your heart think you exercise
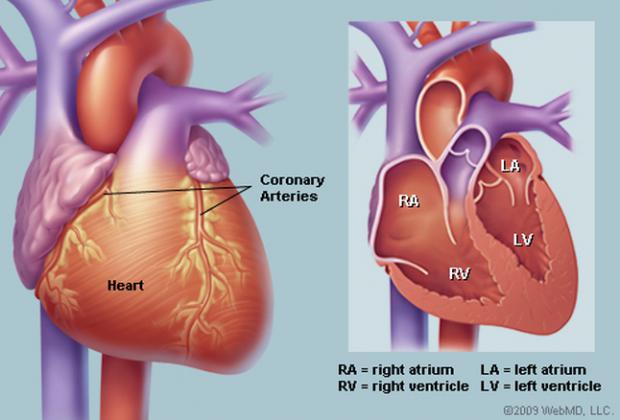
When it needs to pump more blood, the heart can grow in a good way in response to exercise and pregnancy, but after a heart attack, swelling of the heart muscles can lead to further complications. Now, Canadian scientists have found that a protein called cardiotrophin 1 (CT1) can essentially trick the heart into the good kind of growth, and reduce the bad kind.
Heart failure is a life-threatening condition where the organ can't adequately pump blood around the body, and often the only treatment is a transplant. It can be caused by a heart attack that damages muscles in the left side of the organ, or by pulmonary hypertension, whereby high blood pressure in the lungs damages the right side.

 Unbanked In A Connected World
Unbanked In A Connected World

