
Breaking News
 A Jubilant Lindsey Graham Goes Full NeoCon: "You See this Hat?…The Liberation of Cuba is Upon..
A Jubilant Lindsey Graham Goes Full NeoCon: "You See this Hat?…The Liberation of Cuba is Upon..
 The Economic Impact Of This Horrifying War With Iran Is Not Going To Be Pretty
The Economic Impact Of This Horrifying War With Iran Is Not Going To Be Pretty
 EPISODE 466 (MARCH 5, 2026) | THE HIGHWIRE: VACCINE UPTAKE, LIABILITY, AND ALUMINUM...
EPISODE 466 (MARCH 5, 2026) | THE HIGHWIRE: VACCINE UPTAKE, LIABILITY, AND ALUMINUM...
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
More durable and longer lasting lithium-ion batteries with nanosheet anodes
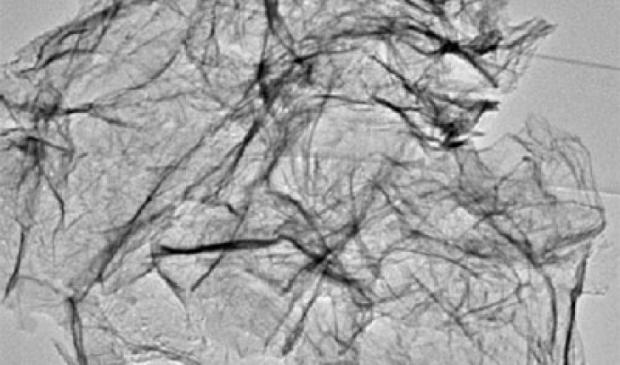
These nanosheets (image on right) are 50,000 times thinner than a sheet of paper, allowing faster charging of power compared to current battery technology. The wide surface area of the nanosheets makes better contact with the electrolyte, thus increasing the storage capacity. The material is also highly durable and does not break easily, which improves the battery shelf life. Existing methods of making metal oxide nanosheets are time-consuming and difficult to scale up.
The IBN researchers came up with a simpler and faster way to synthesize metal oxide nanosheets using graphene oxide. Graphene oxide is a 2D carbon material with chemical reactivity that facilities the growth of metal oxides on its surface.
Graphene oxide was used as the template to grow metal oxides into nanosheet structures via a simple mixing process, followed by heat treatment. The researchers were able to synthesize a wide variety of metal oxides as nanosheets, with control over the composition and properties.

 I resigned from OpenAI.
I resigned from OpenAI. 

