
Breaking News
 A Jubilant Lindsey Graham Goes Full NeoCon: "You See this Hat?…The Liberation of Cuba is Upon..
A Jubilant Lindsey Graham Goes Full NeoCon: "You See this Hat?…The Liberation of Cuba is Upon..
 The Economic Impact Of This Horrifying War With Iran Is Not Going To Be Pretty
The Economic Impact Of This Horrifying War With Iran Is Not Going To Be Pretty
 EPISODE 466 (MARCH 5, 2026) | THE HIGHWIRE: VACCINE UPTAKE, LIABILITY, AND ALUMINUM...
EPISODE 466 (MARCH 5, 2026) | THE HIGHWIRE: VACCINE UPTAKE, LIABILITY, AND ALUMINUM...
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Deep Learning at 15 Petaflops from Intel and partners
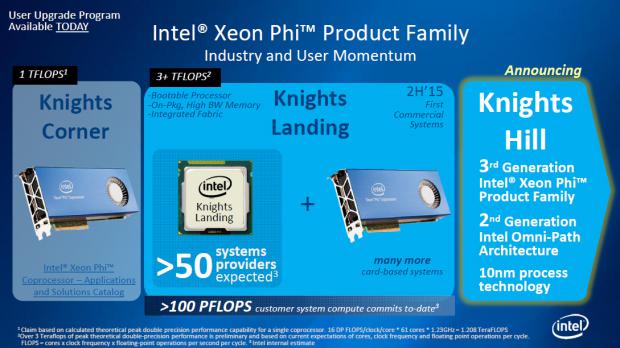
Intel researchers and parters developed supervised convolutional architectures for discriminating signals in high-energy physics data as well as semi-supervised architectures for localizing and
classifying extreme weather in climate data. Our Intelcaffe based implementation obtains ∼2TFLOP/s on a single Cori Phase-II Xeon-Phi node. We use a hybrid strategy employing synchronous node-groups, while using asynchronous communication across groups. They use this strategy to scale training of a single model to ∼9600 Xeon-Phi nodes; obtaining peak performance of 11.73-15.07 PFLOP/s and sustained performance of 11.41-13.27 PFLOP/s. At scale, their HEP architecture produces state-of-the-art classification accuracy on a dataset with 10 Million images, exceeding
that achieved by selections on high-level physics-motivated features. Their semi-supervised architecture successfully extracts weather patterns in a 15TB climate dataset. Their results demonstrate that Deep Learning can be optimized and scaled effectively on many-core, HPC systems.

 I resigned from OpenAI.
I resigned from OpenAI. 

