
Breaking News
DRINK 1 CUP Before Bed for a Smaller Waist
 Nano-magnets may defeat bone cancer and help you heal
Nano-magnets may defeat bone cancer and help you heal
 Dan Bongino Officially Leaves FBI After One-Year Tenure, Says Time at the Bureau Was...
Dan Bongino Officially Leaves FBI After One-Year Tenure, Says Time at the Bureau Was...
 WATCH: Maduro Speaks as He's Perp Walked Through DEA Headquarters in New York
WATCH: Maduro Speaks as He's Perp Walked Through DEA Headquarters in New York
Top Tech News
 Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
Laser weapons go mobile on US Army small vehicles
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Stay cool without electricity:
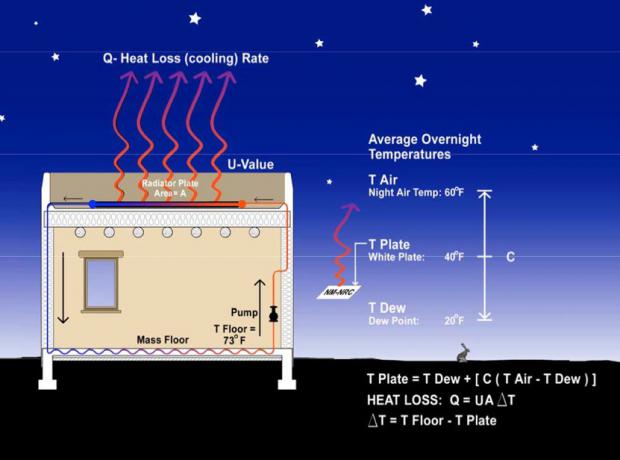
Staying cool during hot or humid weather without racking up a hefty electricity bill could be a reality in the near future. A team of researchers from Stanford University have developed a passive cooling system that sends excess heat towards outer space. Since almost no energy is required to keep them functional, these high-tech optical surfaces could one day help reduce the amount of electricity being consumed by air conditioners and refrigerators.
"This research builds on our previous work with radiative sky cooling but takes it to the next level," explained Shanhui Fan, lead researcher and professor of electrical engineering. "It provides for the first time a high-fidelity technology demonstration of how you can use radiative sky cooling to passively cool a fluid and, in doing so, connect it with cooling systems to save electricity."



