
Breaking News
 Grow Unlimited Protein In A Trash Can. No Soil. No Sunlight. The 5 Min Setup.
Grow Unlimited Protein In A Trash Can. No Soil. No Sunlight. The 5 Min Setup.
 Why Amish Gardens Never Have Pests -- The One "Stick" Method Corporations Hate.
Why Amish Gardens Never Have Pests -- The One "Stick" Method Corporations Hate.
 7 MINUTE BUILD | Off-Grid DIY Underground Earthbag Pantry, Root Cellar, and Storm Shelter
7 MINUTE BUILD | Off-Grid DIY Underground Earthbag Pantry, Root Cellar, and Storm Shelter
 Sedentary Adulthood Increases Biological Stress Levels by Middle Age
Sedentary Adulthood Increases Biological Stress Levels by Middle Age
Top Tech News
 The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
The Pentagon is looking for the SpaceX of the ocean.
 Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
Major milestone by 3D printing an artificial cornea using a specialized "bioink"...
 Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
Scientists at Rice University have developed an exciting new two-dimensional carbon material...
 Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
Footage recorded by hashtag#Meta's AI smart glasses is sent to offshore contractors...
 ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
ELON MUSK: "With something like Neuralink… we effectively become maybe one with the AI."
 DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
DARPA Launches New Program Generative Optogenetics, GO,...
 Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
Anthropic Outpaces OpenAI Revenue 10X, Pentagon vs. Dario, Agents Rent Humans | #234
 Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
Ordering a Tiny House from China, what's the real COST?
 New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
New video may offer glimpse of secret F-47 fighter
 Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
Donut Lab's Solid-State Battery Charges Fast. But Experts Still Have Questions
DNA nanobot created that performs nanomechanical tasks
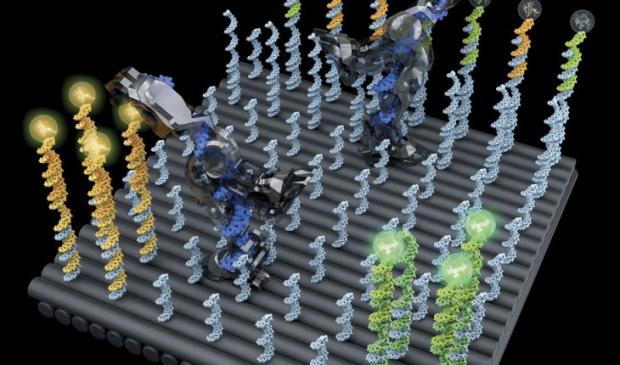
Robots are an important type of molecular machine that automatically carry out complex nanomechanical tasks. DNA molecules are excellent materials for building molecular robots, because their geometric, thermodynamic, and kinetic properties are well understood and highly programmable. So far, the development of DNA robots has been limited to simple functions. Most DNA robots were designed to perform a single function: walking in a controlled direction. A few demonstrations included a second function combined with walking (for example, picking up nanoparticles or choosing a path at a junction). However, these relatively more complex functions were also more difficult to control, and the complexity of the tasks was limited to what the robot can perform within 3 to 12 steps. In addition, each robot design was tailored for a specific task, complicating efforts to develop new robots that perform new tasks by combining functions and mechanisms.



