
Breaking News
6.5x55 Swedish vs. 6.5 Creedmoor: The New 6.5mm Hotness
Best 7mm PRC Ammo: Hunting and Long-Distance Target Shooting
 Christmas Truce of 1914, World War I - For Sharing, For Peace
Christmas Truce of 1914, World War I - For Sharing, For Peace
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Nerve Implant 'Restores Consciousness' To Man In Persistent Vegetative State
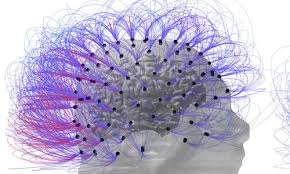
Stimulation of the vagus nerve allows patient who had been in a persistent vegetative state for 15 years to track objects with his eyes and respond to simple requests.
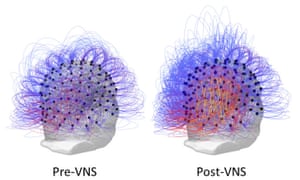
On the right, the warmer colours indicate an increase in connectivity following vagus nerve stimulation among brain regions responsible for planned movements, spatial reasoning and attention. Illustration: Corazzol et al.
A 35-year-old man who had been in a persistent vegetative state (PVS) for 15 years has shown signs of consciousness after receiving a pioneering therapy involving nerve stimulation.
The treatment challenges a widely-accepted view that there is no prospect of a patient recovering consciousness if they have been in PVS for longer than 12 months.
Since sustaining severe brain injuries in a car accident, the man had been completely unaware of the world around him. But when fitted with an implant to stimulate the vagus nerve, which travels into the brain stem, the man appeared to flicker back into a state of consciousness.
He started to track objects with his eyes, began to stay awake while being read a story and his eyes opened wide in surprise when the examiner suddenly moved her face close to the patient's. He could even respond to some simple requests, such as turning his head when asked – although this took about a minute.
Angela Sirigu, who led the work at the Institut des Sciences Cognitives Marc Jeannerod in Lyon, France, said: "He is still paralysed, he cannot talk, but he can respond. Now he is more aware."
Niels Birbaumer, of the University of Tübingen and a pioneer of brain-computer interfaces to help patients with neurological disorders communicate, said the findings, published in the journal Current Biology, raised pressing ethical issues. "Many of these patients may and will have been neglected, and passive euthanasia may happen often in a vegetative state," he said. "This paper is a warning to all those believing that this state is hopeless after a year."
The vagus nerve, which the treatment targeted, connects the brain to almost all the vital organs in the body, running from the brain stem down both sides of the neck, across the chest and into the abdomen. In the brain, it is linked directly to two regions known to play roles in alertness and consciousness.

 The State's Last Stand
The State's Last Stand


