
Breaking News
 Christmas Truce of 1914, World War I - For Sharing, For Peace
Christmas Truce of 1914, World War I - For Sharing, For Peace
 The Roots of Collectivist Thinking
The Roots of Collectivist Thinking
 What Would Happen if a Major Bank Collapsed Tomorrow?
What Would Happen if a Major Bank Collapsed Tomorrow?
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
IBM has 50 qubit prototype chip which should be close to Quantum Supremacy
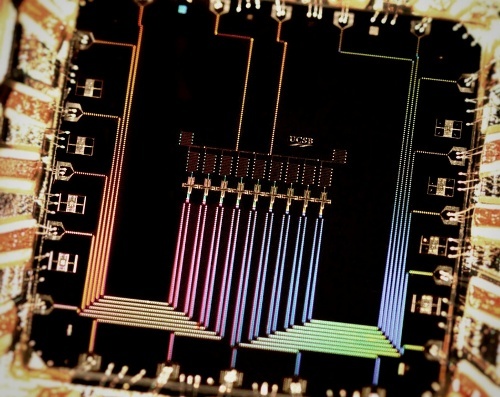
Doubling the transistors on a regular chip might achieve double the performance doubling the qubits on a quantum computer can provide an exponential speedup depending upon the kind of problem it is trying to solve. Dwave has shown speed ups of 10,000 time or more by doubling the qubits in their quantum annealing systems.
IBM Q scientists have successfully built and measured a 50 qubit processor prototype. Expanding on the 20 qubit architecture, it will be the next-gen IBM Q system. IBM aims to demonstrate capabilities beyond today's classical systems with systems of this size.
The first IBM Q systems available online to clients will have a 20 qubit processor. This new device's advanced design, connectivity and packaging delivers industry-leading coherence times (the amount of time to perform quantum computations), which are double that of IBM's 5 and 16 qubit processors available to the public on the IBM Q experience.

 The State's Last Stand
The State's Last Stand


