
Breaking News
 James O'Keefe: My entire speech at AmericaFest 2025. We're not stopping. Join us to expose..
James O'Keefe: My entire speech at AmericaFest 2025. We're not stopping. Join us to expose..
 U.S. vs. Chinese Military Comparison – Focus on Asia-Taiwan Scenario
U.S. vs. Chinese Military Comparison – Focus on Asia-Taiwan Scenario
 DoJ Sues Four More States for Failing To Produce Voter-roll Data
DoJ Sues Four More States for Failing To Produce Voter-roll Data
 World's Largest Aviation Giant Abandons Google Over Security Concerns
World's Largest Aviation Giant Abandons Google Over Security Concerns
Top Tech News
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
 A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
 Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
This Is What The First Soft Artificial Heart Looks Like
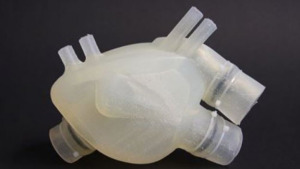
A doctoral student named Nicholas Cohrs created it along with a group from ETH Zurich using 3D printing but it's a work in progress.
"Our goal is to develop an artificial heart that is roughly the same size as the patient's own one and which imitates the human heart as closely as possible in form and function," said Cohrs.
There is still one major issue with it.
The heart only lasts about 3,000 heartbeats. That's roughly 30 to 45 minutes.
Why?
The material can't seem to stand the strain.
Despite that, it still shows the potential of artificial organs possibly saving lives in the future.
"A well-functioning artificial heart is a real necessity: about 26 million people worldwide suffer from heart failure while there is a shortage of donor hearts. Artificial blood pumps help to bridge the waiting time until a patient receives a donor heart or their own heart recovers," said Cohrs.

 Advanced Propulsion Resources Part 1 of 2
Advanced Propulsion Resources Part 1 of 2

