
Breaking News
 Holy Sh*t...Now Deutsche Bank AND Morgan Stanley!?
Holy Sh*t...Now Deutsche Bank AND Morgan Stanley!?
 Amyloid microclots were found in 100% of the C-19 inoculated in a new study.
Amyloid microclots were found in 100% of the C-19 inoculated in a new study.
 If The "Iranians" Attack Here…
If The "Iranians" Attack Here…
 Kraken's surprise Fed win may harken onslaught of crypto firms with narrow Fed access
Kraken's surprise Fed win may harken onslaught of crypto firms with narrow Fed access
Top Tech News
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
Will Yann LeCun Provide The Next Breakthrough In AI?
 Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
Human Brain Cells Merge With Silica To Play DOOM
 Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
Solar And Storage Could Reshape Rural Electricity Markets
 With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
With World Seemingly At War, DARPA Finds Time To Unveil The X-76
 The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
The world's first diesel plug-in hybrid pickup truck is here
 US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
US advances nuclear revival with approval of Natrium Gen IV reactor
 Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
Your Contractor Doesn't Want Me To Show You This!
 CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
CEO of Blacklisted AI Company Anthropic, Dario Amodei Says His AI Models 'May Have Gained...
Nanoparticles detect and track cancer months before traditional imaging techniques
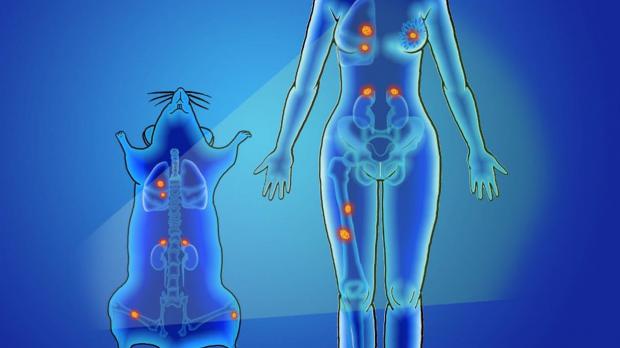
One of the major downsides of current cancer diagnosis technologies is that a tumor can often grow to a damaging size by the time imaging methods detect it. Catching a cancer when it metastasizes can also be tricky as doctors generally won't know the disease has spread until it's too late.
This new detection method involves injecting a subject with nanoparticles that emit short-wave infrared light. These nanoparticles travel through the bloodstream and are designed to stick to specific cancer cells. In early mouse experiments the particles accurately identified and tracked breast cancer cells as they spread to several other locations in the animal's body.
"We've always had this dream that we can track the progression of cancer in real time, and that's what we've done here," says corresponding author of the study Prabhas V. Moghe. "We've tracked the disease in its very incipient stages."

 Renewable Water From Air.
Renewable Water From Air.

