
Breaking News
 Christmas Truce of 1914, World War I - For Sharing, For Peace
Christmas Truce of 1914, World War I - For Sharing, For Peace
 The Roots of Collectivist Thinking
The Roots of Collectivist Thinking
 What Would Happen if a Major Bank Collapsed Tomorrow?
What Would Happen if a Major Bank Collapsed Tomorrow?
Top Tech News
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
 A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
 Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Ion beam controlled to etch single silicon atom depth
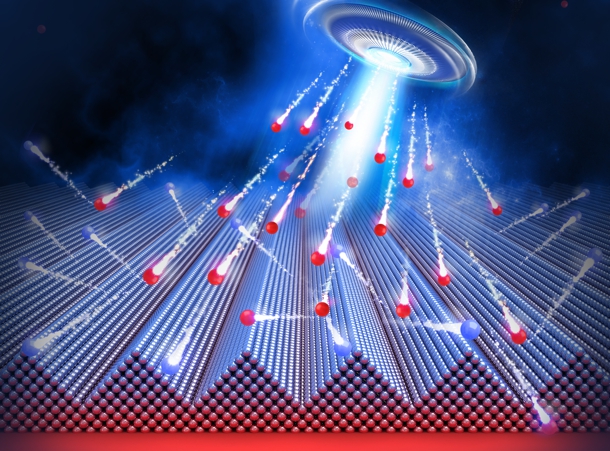
The beams can create tiny features in the lateral dimensions—length and width, but to create the next generation of nanometer-scale devices, the energetic ions must precisely control the features in the vertical dimension—depth. Now, researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have demonstrated that a standard ion-beam technique can be fine-tuned to make structures with depths controlled to within the diameter of a single silicon atom.
Above – nanofluidic staircase machined with subnanometer precision by a focused ion beam separates nanoparticles by size. The device is also a reference material to accurately measure nanoparticle size and compare it to optical brightness, which could aid in the quality control of consumer products. Credit: NIST

 The State's Last Stand
The State's Last Stand


