
Breaking News
 COMEX Silver: 21 Days Until 429 Million Ounces of Demand Meets 103 Million Supply. (March Crisis)
COMEX Silver: 21 Days Until 429 Million Ounces of Demand Meets 103 Million Supply. (March Crisis)
 Marjorie Taylor Greene: MAGA Was "All a Lie," "Isn't Really About America or the
Marjorie Taylor Greene: MAGA Was "All a Lie," "Isn't Really About America or the
 Why America's Two-Party System Will Never Threaten the True Political Elites
Why America's Two-Party System Will Never Threaten the True Political Elites
 Generation Now #7 – Youth in Davos | Youth Pulse 2026 | Skills That Matter
Generation Now #7 – Youth in Davos | Youth Pulse 2026 | Skills That Matter
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
Yttrium hydrogen compound should be room temperature superconductor when under extreme pressure
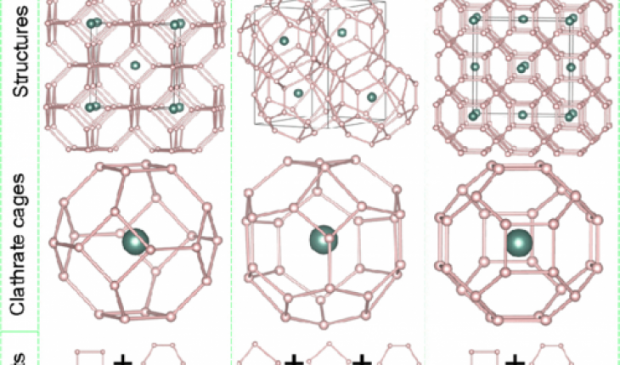
A collaboration between the University of Cambridge and Jilin University has published the results of a computational search for materials that might superconduct at even higher temperatures.
An extensive search for the stable structures and compositions of rare earth hydrides was performed using first principles density functional theory based methods. The superconducting transition temperatures for the stable metallic compounds were calculated using the same theoretical techniques that were used to anticipate the superconductivity in dense hydrogen sulphide. The highest temperatures were predicted for pressures that are around those found in the center of the Earth. It is a challenge for the future to find materials that superconduct at high temperatures and everyday low pressures.



