
Breaking News
6.5x55 Swedish vs. 6.5 Creedmoor: The New 6.5mm Hotness
Best 7mm PRC Ammo: Hunting and Long-Distance Target Shooting
 Christmas Truce of 1914, World War I - For Sharing, For Peace
Christmas Truce of 1914, World War I - For Sharing, For Peace
Top Tech News
 EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
EngineAI T800: Born to Disrupt! #EngineAI #robotics #newtechnology #newproduct
 This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
This Silicon Anode Breakthrough Could Mark A Turning Point For EV Batteries [Update]
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
AgeX and Insilico reveal genes implicated in tissue regeneration, cancer, and aging
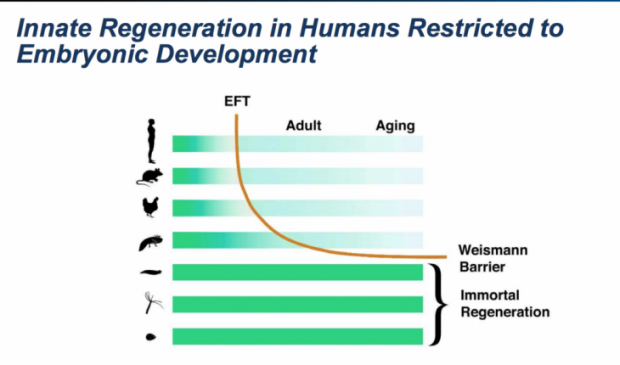
The study, by scientists at AgeX and BioTime, in collaboration with Insilico Medicine, utilized artificial intelligence (AI) technology to parse millions of gene expression data points to decipher the complex mechanisms controlling natural tissue regeneration. The results, published in the peer-reviewed scientific journal Oncotarget, showed that the candidate genes are expressed differently in tissues early in development when they are capable of regeneration compared to later in life when regeneration can no longer take place. Surprisingly, some of the genes, including one highlighted in the study, COX7A1, displayed a rare profile of being nearly universally dysregulated in diverse types of cancer. The discoveries may lead to novel strategies to induce Tissue Regeneration (iTRTM) in the context of trauma or age-related degenerative disease, as well as treat and diagnose cancer.

 The State's Last Stand
The State's Last Stand


