
Breaking News
 2 Hours of Retro Sci-Fi Christmas Songs | Atomic-Age Christmas at a Snowy Ski Resort
2 Hours of Retro Sci-Fi Christmas Songs | Atomic-Age Christmas at a Snowy Ski Resort
 Alternative Ways to Buy Farmland
Alternative Ways to Buy Farmland
 LED lights are DEVASTATING our bodies, here's why | Redacted w Clayton Morris
LED lights are DEVASTATING our bodies, here's why | Redacted w Clayton Morris
Top Tech News
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
 A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
 Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Human skeletal muscle grown from stem cells
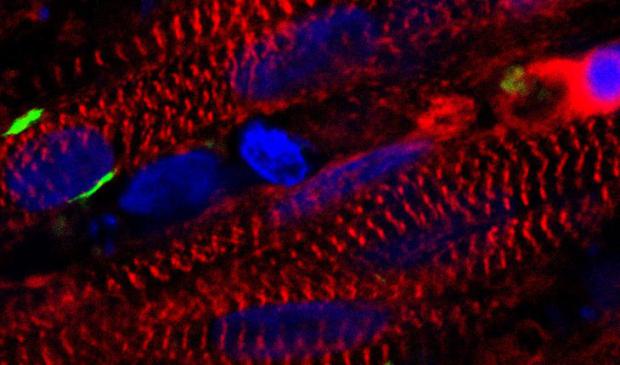
The advance builds on work published in 2015 when researchers at Duke University grew the first functioning human muscle tissue from cells obtained from muscle biopsies. The ability to start from cellular scratch using non-muscle tissue will allow scientists to grow far more muscle cells, provide an easier path to genome editing and cellular therapies, and develop individually tailored models of rare muscle diseases for drug discovery and basic biology studies.
Above – A stained cross section of the new muscle fibers. The red cells are muscle cells, the green areas are receptors for neuronal input, and the blue patches are cell nuclei.
"Starting with pluripotent stem cells that are not muscle cells, but can become all existing cells in our body, allows us to grow an unlimited number of myogenic progenitor cells," said Nenad Bursac, professor of biomedical engineering at Duke University. "These progenitor cells resemble adult muscle stem cells called 'satellite cells' that can theoretically grow an entire muscle starting from a single cell."

 $100 SILVER CONFIRMED?
$100 SILVER CONFIRMED?

