
Breaking News
 2 Hours of Retro Sci-Fi Christmas Songs | Atomic-Age Christmas at a Snowy Ski Resort
2 Hours of Retro Sci-Fi Christmas Songs | Atomic-Age Christmas at a Snowy Ski Resort
 Alternative Ways to Buy Farmland
Alternative Ways to Buy Farmland
 LED lights are DEVASTATING our bodies, here's why | Redacted w Clayton Morris
LED lights are DEVASTATING our bodies, here's why | Redacted w Clayton Morris
Top Tech News
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
 A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
 Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Platelet coated stem cells Could Offer Targeted Heart Repair
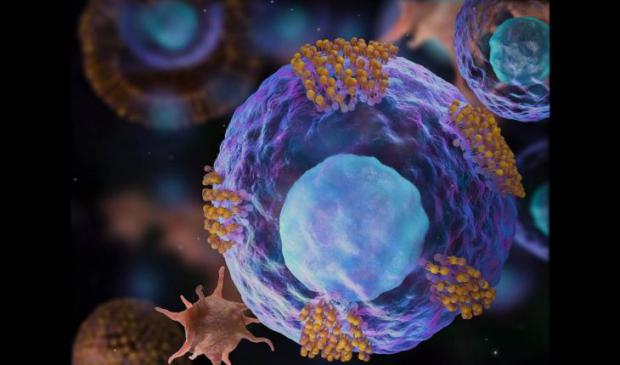
In a new pilot study using an animal model, North Carolina State University researcher Ke Cheng and his team show that "decorating" cardiac stem cells with platelet nanovesicles can increase the stem cells' ability to find and remain at the site of heart attack injury and enhance their effectiveness in treatment.
"Platelets can home in on an injury site and stay there, and even in some cases recruit a body's own naturally occurring stem cells to the site, but they are a double-edged sword," says Cheng, associate professor of veterinary medicine and associate professor in the NC State/UNC Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering. "That's because once the platelets arrive at the site of injury, they trigger the coagulation processes that cause clotting. In a heart-attack injury, blood clots are the last thing that you want."

 $100 SILVER CONFIRMED?
$100 SILVER CONFIRMED?

