
Breaking News
 Why are young women attracted to older men? Men, watch and learn!
Why are young women attracted to older men? Men, watch and learn!
 Voter Fraud Is About To Explode: ITS BLOWING UP IN THEIR FACES thanks to Trump and Tulsi
Voter Fraud Is About To Explode: ITS BLOWING UP IN THEIR FACES thanks to Trump and Tulsi
 Ahead of US-Iran Talks, Netanyahu Tells Cabinet 'Conditions' Could Lead to Regime Change...
Ahead of US-Iran Talks, Netanyahu Tells Cabinet 'Conditions' Could Lead to Regime Change...
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
Device creates negative mass and a new way to generate lasers
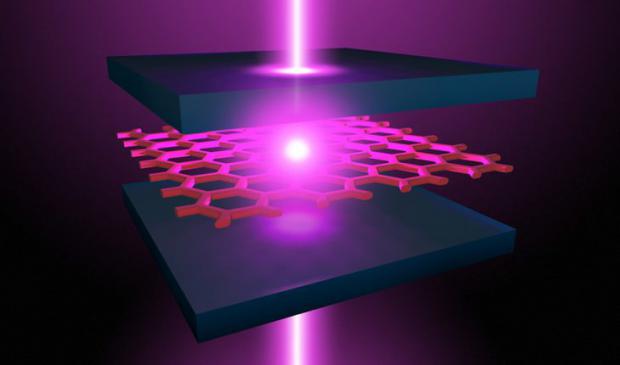
Now University of Rochester researchers have succeeded in creating particles with negative mass in an atomically thin semiconductor, by causing it to interact with confined light in an optical microcavity.
Above – In this optical microcavity, created by the lab of Nick Vamivakas, confined light interacts with an atomically thin semiconductor to create particles with negative mass. The device also presents "a way to generate laser light with an incrementally small amount of power," says Vamivakas, an associate professor of quantum optics and quantum physics at Rochester's Institute of Optics. (Illustration by Michael Osadciw/University of Rochester)
This alone is "interesting and exciting from a physics perspective," says Nick Vamivakas, an associate professor of quantum optics and quantum physics at Rochester's Institute of Optics. "But it also turns out the device we've created presents a way to generate laser light with an incrementally small amount of power."



