
Breaking News
 Why are young women attracted to older men? Men, watch and learn!
Why are young women attracted to older men? Men, watch and learn!
 Voter Fraud Is About To Explode: ITS BLOWING UP IN THEIR FACES thanks to Trump and Tulsi
Voter Fraud Is About To Explode: ITS BLOWING UP IN THEIR FACES thanks to Trump and Tulsi
 Ahead of US-Iran Talks, Netanyahu Tells Cabinet 'Conditions' Could Lead to Regime Change...
Ahead of US-Iran Talks, Netanyahu Tells Cabinet 'Conditions' Could Lead to Regime Change...
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
Top Tech News
 How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
How underwater 3D printing could soon transform maritime construction
 Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
Smart soldering iron packs a camera to show you what you're doing
 Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
Look, no hands: Flying umbrella follows user through the rain
 Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
Critical Linux Warning: 800,000 Devices Are EXPOSED
 'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
'Brave New World': IVF Company's Eugenics Tool Lets Couples Pick 'Best' Baby, Di
 The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
The smartphone just fired a warning shot at the camera industry.
 A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
A revolutionary breakthrough in dental science is changing how we fight tooth decay
 Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
Docan Energy "Panda": 32kWh for $2,530!
 Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
Rugged phone with multi-day battery life doubles as a 1080p projector
 4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
4 Sisters Invent Electric Tractor with Mom and Dad and it's Selling in 5 Countries
Graphene Nanoribbons are 100 times brighter than previous single molecule devices
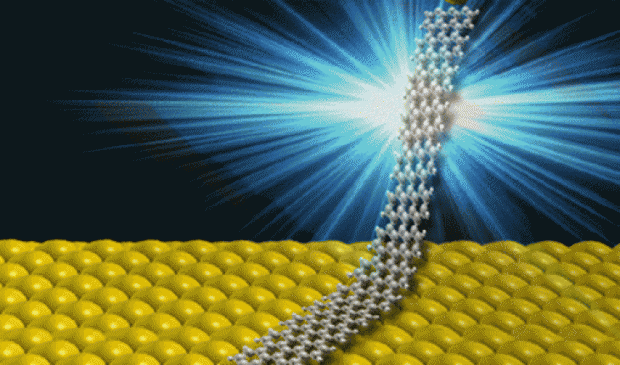
Optical emission was up to 10 million photons per second, about 100 times more intense than the emission measured for previous single-molecular optoelectronic devices.
The energy shift of the main peak changes as a function of the voltage, which provides a way to tune the color of the light.
The researchers will investigate the impact of defects and GNR aspect ratio (width) on emission. They want to integrate graphene nanoribbons devices into larger circuitry to create bright, robust, and controllable graphene-based light-emitting devices.
Abstract
Thanks to their highly tunable band gaps, graphene nanoribbons (GNRs) with atomically precise edges are emerging as mechanically and chemically robust candidates for nanoscale light emitting devices of modulable emission color. While their optical properties have been addressed theoretically in depth, only few experimental studies exist, limited to ensemble measurements and without any attempt to integrate them in an electronic-like circuit.



