
Breaking News
 2 Hours of Retro Sci-Fi Christmas Songs | Atomic-Age Christmas at a Snowy Ski Resort
2 Hours of Retro Sci-Fi Christmas Songs | Atomic-Age Christmas at a Snowy Ski Resort
 Alternative Ways to Buy Farmland
Alternative Ways to Buy Farmland
 LED lights are DEVASTATING our bodies, here's why | Redacted w Clayton Morris
LED lights are DEVASTATING our bodies, here's why | Redacted w Clayton Morris
Top Tech News
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
 A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
 Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Bizarre metal conducts electricity without heating up
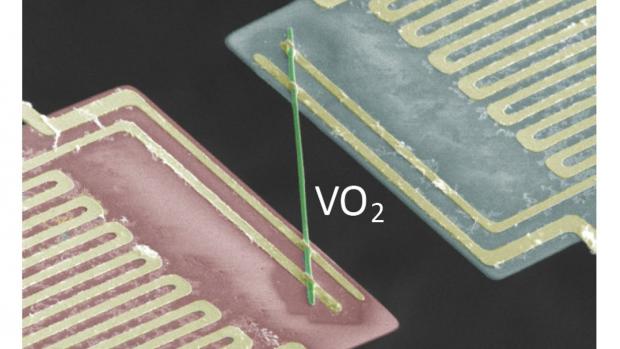
Such a strange property may be expected to occur in conductors operating at cryogenic temperatures, but a team of researchers led by the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory claims to have discovered this unique property in vanadium dioxide at temperatures of around 67 °C (153 °F).
Of all the metals found on Earth, most are both good conductors of heat and electricity. This is because classic physics dictates that their electrons are responsible for both the movement of electrical current and the transfer of heat. This correlation between electrical and thermal conductivity is dictated by the Wiedemann-Franz Law, which basically says that metals that conduct electricity well are also good conductors of heat.
However, metallic vanadium dioxide (VO2) seems to be different. When the researchers passed an electrical current through nanoscale rods of single-crystal VO2, and thermal conductivity was measured, the heat produced by electron movement was actually ten times less than that predicted by calculations of the Wiedemann-Franz Law.

 $100 SILVER CONFIRMED?
$100 SILVER CONFIRMED?

