
Breaking News
 2 Hours of Retro Sci-Fi Christmas Songs | Atomic-Age Christmas at a Snowy Ski Resort
2 Hours of Retro Sci-Fi Christmas Songs | Atomic-Age Christmas at a Snowy Ski Resort
 Alternative Ways to Buy Farmland
Alternative Ways to Buy Farmland
 LED lights are DEVASTATING our bodies, here's why | Redacted w Clayton Morris
LED lights are DEVASTATING our bodies, here's why | Redacted w Clayton Morris
Top Tech News
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
 A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
 Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Programmed DNA nanorobots to shrink cancer tumors by cutting off their blood supply
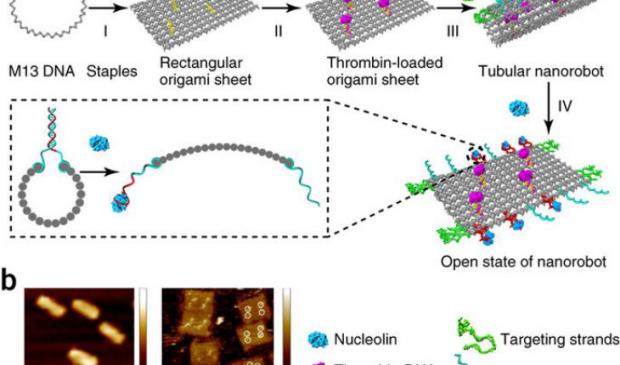
n a major advancement in nanomedicine, Arizona State University scientists, in collaboration with researchers from the National Center for Nanoscience and Technology (NCNST) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, have successfully programmed nanorobots to shrink tumors by cutting off their blood supply.
"We have developed the first fully autonomous, DNA robotic system for a very precise drug design and targeted cancer therapy," said Hao Yan, director of the ASU Biodesign Institute's Center for Molecular Design and Biomimetics and the Milton Glick Professor in the School of Molecular Sciences.
"Moreover, this technology is a strategy that can be used for many types of cancer, since all solid tumor-feeding blood vessels are essentially the same," Yan said.
Seek and destroy
Yan is an expert in the field of DNA origami, which in the past two decades has developed atomic-scale manufacturing to build more and more complex structures.
The bricks to build their structures come from DNA, which can self-fold into all sorts of shapes and sizes — all at a scale 1,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair — in the hopes of one day revolutionizing computing, electronics and medicine.
That one day may be coming a bit faster than anticipated.
Nanomedicine is a new branch of medicine that seeks to combine the promise of nanotechnology to open up entirely new avenues for treatments, such as making minuscule, molecule-sized nanoparticles to diagnose and treat difficult diseases, especially cancer.
Read More...

 $100 SILVER CONFIRMED?
$100 SILVER CONFIRMED?

