
Breaking News
 The #1 Most Dangerous Fat in the World!
The #1 Most Dangerous Fat in the World!
 Is $140K the New Poverty Line? Is This the End of America's Middle Class?
Is $140K the New Poverty Line? Is This the End of America's Middle Class?
 Here Are the NEWLY RELEASED Epstein Images Tied to Powerful Democrats
Here Are the NEWLY RELEASED Epstein Images Tied to Powerful Democrats
 Joe Biden Still Struggling to Raise Money for Presidential Library – No New Donations...
Joe Biden Still Struggling to Raise Money for Presidential Library – No New Donations...
Top Tech News
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
 A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
 Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
 Advanced Propulsion Resources Part 1 of 2
Advanced Propulsion Resources Part 1 of 2
 PulsarFusion a forward-thinking UK aerospace company, is pushing the boundaries of space travel...
PulsarFusion a forward-thinking UK aerospace company, is pushing the boundaries of space travel...
 Dinky little laser box throws big-screen entertainment from inches away
Dinky little laser box throws big-screen entertainment from inches away
 'World's first' sodium-ion flashlight shines bright even at -40 ºF
'World's first' sodium-ion flashlight shines bright even at -40 ºF
Bleached-white nanowood material promises exceptional insulating properties
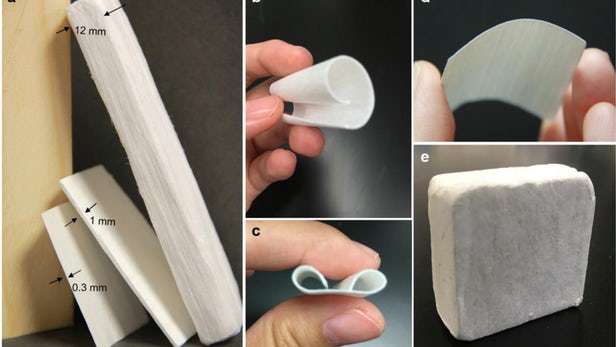
"Nanowood" as the team calls it, is produced by taking certain cuts of regular wood –American basswood in initial trials – and chemically removing all the lignin from it. Lignin contributes the yellow/brown color and hardness you'd normally associate with wood. It's removed entirely when making perfectly white paper that doesn't yellow as it ages.
In fact, the process for producing nanowood is very similar to making paper – the wood is cut, paying special attention to its grain, and then it's boiled in sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfite, then treated in hydrogen peroxide to remove lignin and most of the hemicellulose, and then freeze-dried to maintain the structure of the wood, instead of mashed up as you would to produce paper.
With the lignin taken out of a block of wood, what you're left with is a lightweight, white bundle of cellulose fibers – the scaffold-like structure of the wood itself.
These fibers not only act as extremely effective insulators that are significantly better at blocking heat than the styrene- or silica-based materials typically used in home insulation, but their tubular shape also gives them anisotropic properties. Heat can conduct fairly freely in line with the fibers, but is very effectively blocked in any other direction. So designers can use this property to channel heat around the place as they see fit, and block it elsewhere, just by changing the orientation of the nanowood fibers.



