
Breaking News
 The Self-Sufficiency Myth No One Talks About
The Self-Sufficiency Myth No One Talks About
 We Investigated The Maui Fires and The Cover-Up is Worse Than We Thought | Redacted
We Investigated The Maui Fires and The Cover-Up is Worse Than We Thought | Redacted
 The Amish Secret to Keeping Pests Out of Your Garden Forever
The Amish Secret to Keeping Pests Out of Your Garden Forever
 Scott Ritter: Full-Scale War as Iran Attacks All U.S. Targets
Scott Ritter: Full-Scale War as Iran Attacks All U.S. Targets
Top Tech News
 US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
US particle accelerators turn nuclear waste into electricity, cut radioactive life by 99.7%
 Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
Blast Them: A Rutgers Scientist Uses Lasers to Kill Weeds
 H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
H100 GPUs that cost $40,000 new are now selling for around $6,000 on eBay, an 85% drop.
 We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
We finally know exactly why spider silk is stronger than steel.
 She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
She ran out of options at 12. Then her own cells came back to save her.
 A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
A cardiovascular revolution is silently unfolding in cardiac intervention labs.
 DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
DARPA chooses two to develop insect-size robots for complex jobs like disaster relief...
 Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
Multimaterial 3D printer builds fully functional electric motor from scratch in hours
 WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
WindRunner: The largest cargo aircraft ever to be built, capable of carrying six Chinooks
A Real World 'Star Trek' Replicator Is Now Possible Thanks To New Breakthrough
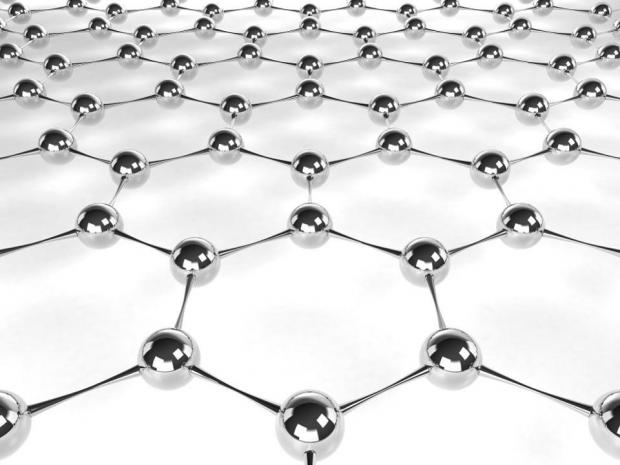
New York-based Mattershift has managed to create large-scale carbon nanotube (CNT) membranes that are able to combine and separate individual molecules.
"This technology gives us a level of control over the material world that we've never had before," said Mattershift Founder and CEO Dr. Rob McGinnis in a release. "For example, right now we're working to remove CO2 from the air and turn it into fuels. This has already been done using conventional technology, but it's been too expensive to be practical. Using our tech, I think we'll be able to produce carbon-zero gasoline, diesel, and jet fuels that are cheaper than fossil fuels."
CNTs have been identified as holding promise for a number of potential applications, from better golf clubs, fuels and medicines to far-out concepts like space elevators. A study published this week in the journal Science Advances confirms that Mattershift's large CNT membranes perform as well as the small prototypes we've seen so far.

 RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?
RNA Crop Spray: Should We Be Worried?

