
Breaking News
 Pentagon To Send 200 Troops to Nigeria
Pentagon To Send 200 Troops to Nigeria
 Trump Says He May Send Second Aircraft Carrier to Middle East To Prepare for Potential Attack...
Trump Says He May Send Second Aircraft Carrier to Middle East To Prepare for Potential Attack...
 A Market Crash and Recession Are Bullish, Not Bearish
A Market Crash and Recession Are Bullish, Not Bearish
 What Are They Still Hiding? New Epstein Questions Point to a Much Bigger Cover-Up
What Are They Still Hiding? New Epstein Questions Point to a Much Bigger Cover-Up
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
ESA Is Building an Air Breathing Space Thruster For Satellites
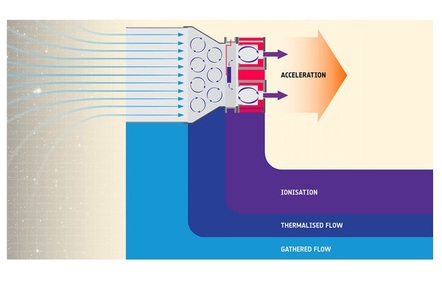
Perhaps outer space's most defining characteristic is the lack of air. The vacuum of space, largely devoid of molecules, makes the European Space Agency's new efforts to build an air-breathing thruster a significant challenge. The space agency recently hit a milestone developing a the new propulsion technology, however, building and testing a thruster in space-like conditions on the ground.
The ESA has been studying air-breathing electric thrusters (ABET) for over a decade. In 2007, a study concluded that the technology "could provide a promising innovative solution" for low Earth orbit (LEO) travel. In this low orbit around the planet, the upper atmosphere is actually thick enough to drag on spacecraft, requiring fuel thrusters to periodically lift satellites to keep them in orbit. An air-breathing thruster could collect these molecules and accelerate them out the back to achieve propulsion, allowing satellites to orbit for longer.



