
Breaking News
 An $11 TRILLION Systemic Risk is Coming in Late March
An $11 TRILLION Systemic Risk is Coming in Late March
 Beneath Greenland's vast ice sheet lies one of Earth's most ancient geological treasures:
Beneath Greenland's vast ice sheet lies one of Earth's most ancient geological treasures:
 Remember the names of every Republican member of Congress who votes no today...
Remember the names of every Republican member of Congress who votes no today...
Top Tech News
 Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
 World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
 New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
 Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
 Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
 Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
 US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
 Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
 The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
New chemical compound 'stops common cold in its tracks'
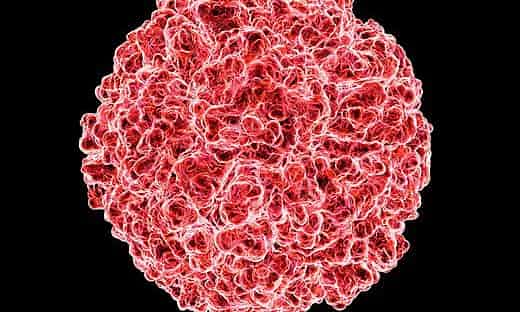
It's a conundrum that has stumped scientists for centuries, but now researchers say they have taken a tantalising step forward in the quest to tackle the common cold.
The scourge of workplace, home and school playground, the common cold is predominantly caused by the rhinovirus. But attempts to thwart the pathogen by vaccination or antiviral drugs face a number of difficulties – not least because the virus comes in many forms and can mutate rapidly leading to drug resistance.
But now scientists say they have discovered a way to nobble the virus that could one day help those with conditions such as asthma and cystic fibrosis, for whom a cold is not merely a nuisance but a serious health risk.

 The Price of Safety
The Price of Safety Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this

