
Breaking News
 Windows 11 QEMU/KVM Installation Guide in Linux Including TPM and Secure Boot
Windows 11 QEMU/KVM Installation Guide in Linux Including TPM and Secure Boot
 Silver: US Mint-Delays and Costco Limits Surface
Silver: US Mint-Delays and Costco Limits Surface
 Boots on the Ground...The news is getting worse so keep prepping.
Boots on the Ground...The news is getting worse so keep prepping.
 O'Keefe Media Group: Secret Service Agent Assigned to Vance Leaks Sensitive Information
O'Keefe Media Group: Secret Service Agent Assigned to Vance Leaks Sensitive Information
Top Tech News
 Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
 World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
 New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
 Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
 Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
 Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
 US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
 Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
 The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
Material could regenerate dental enamel
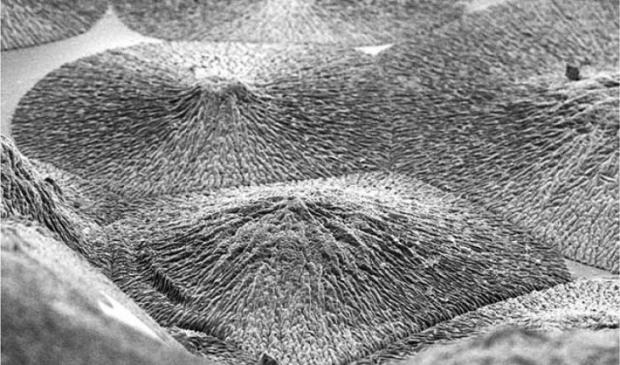
Enamel, located on the outer part of our teeth, is the hardest tissue in the body and enables our teeth to function for a large part of our lifetime despite biting forces, exposure to acidic foods and drinks and extreme temperatures. This remarkable performance results from its highly organised structure.
However, unlike other tissues of the body, enamel cannot regenerate once it is lost, which can lead to pain and tooth loss. These problems affect more than 50 percent of the world's population and so finding ways to recreate enamel has long been a major need in dentistry.
this new approach can create materials with remarkable precision and order that look and behave like dental enamel.
The materials could be used for a wide variety of dental complications such as the prevention and treatment of tooth decay or tooth sensitivity – also known as dentin hypersensitivity.

 Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this

