
Breaking News
 Silver up over $2.26... Today! $71.24 (and Gold close to $4500)
Silver up over $2.26... Today! $71.24 (and Gold close to $4500)
 GARLAND FAVORITO: More and more fraud from the 2020 election in Fulton County, Georgia...
GARLAND FAVORITO: More and more fraud from the 2020 election in Fulton County, Georgia...
 Rep. Matt Gaetz tells Tucker Carlson that agents of the Israeli govt tried to blackmail his...
Rep. Matt Gaetz tells Tucker Carlson that agents of the Israeli govt tried to blackmail his...
 Trump: We need Greenland for national security… you have Russian and Chinese ships all over...
Trump: We need Greenland for national security… you have Russian and Chinese ships all over...
Top Tech News
 Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
Travel gadget promises to dry and iron your clothes – totally hands-free
 Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
Perfect Aircrete, Kitchen Ingredients.
 Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
Futuristic pixel-raising display lets you feel what's onscreen
 Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
Cutting-Edge Facility Generates Pure Water and Hydrogen Fuel from Seawater for Mere Pennies
 This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
This tiny dev board is packed with features for ambitious makers
 Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
Scientists Discover Gel to Regrow Tooth Enamel
 Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
Vitamin C and Dandelion Root Killing Cancer Cells -- as Former CDC Director Calls for COVID-19...
 Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
Galactic Brain: US firm plans space-based data centers, power grid to challenge China
 A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
A microbial cleanup for glyphosate just earned a patent. Here's why that matters
 Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Japan Breaks Internet Speed Record with 5 Million Times Faster Data Transfer
Memristor based equation solver could cut energy used by 100 times for longer lasting smartphones
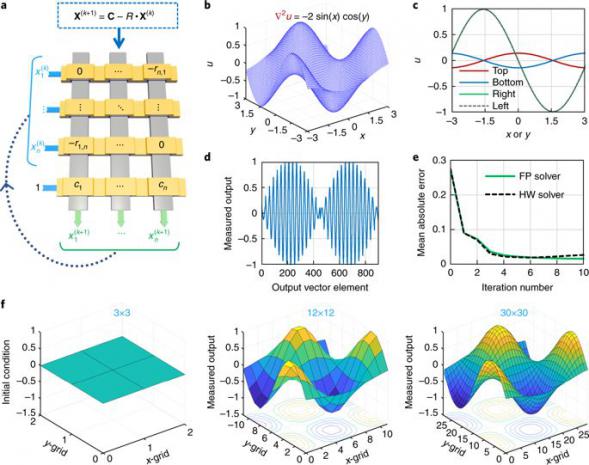
The Nanoelectronics group, University of Michigan, got around this problem by digitizing the current outputs—defining current ranges as specific bit values (i.e., 0 or 1). The team was also able to map large mathematical problems into smaller blocks within the array, improving the efficiency and flexibility of the system.
Computers with these new blocks, which the researchers call "memory-processing units," could be particularly useful for implementing machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms. They are also well suited to tasks that are based on matrix operations, such as simulations used for weather prediction. The simplest mathematical matrices, akin to tables with rows and columns of numbers, can map directly onto the grid of memristors.
nce the memristors are set to represent the numbers, operations that multiply and sum the rows and columns can be taken care of simultaneously, with a set of voltage pulses along the rows. The current measured at the end of each column contains the answers.



