
Breaking News
The Criminality Buried In The Epstein Files Is Worse Than Anyone Thought,...
 A Critical Review of Impacts of Greenhouse Gas Emissions on the U.S. Climate
A Critical Review of Impacts of Greenhouse Gas Emissions on the U.S. Climate
 The Great Reject is Upon Us! - #SolutionsWatch
The Great Reject is Upon Us! - #SolutionsWatch
 Google is issuing a call to action:
Google is issuing a call to action:
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
New spin on heat shields could cut cost of spacecraft
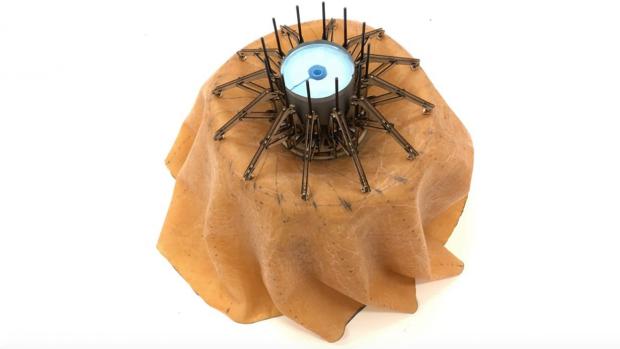
Although some approaches to such shields can be heavy and/or complex, a University of Manchester PhD student has developed one that's simple, cheap and lightweight.
As a spacecraft plummets through a planet's atmosphere, the friction of the air against the rapidly-passing underside of the craft causes heat to build up. Heat shields serve to dissipate that heat, keeping it from damaging the spacecraft itself, while also helping to slow the spacecraft's descent by creating aerodynamic drag.
Presently-used shields include ones that inflate when needed, or that are mechanically deployed. Rui Wu, however, created a prototype that's a little different.
Made of a flexible, strong and heat-resistant material that folds down when not in use, his shield automatically starts spinning like a samara-type tree seed when exposed to the onrush of air that a spacecraft would experience when dropping through a planet's atmosphere.



