
Breaking News
 Zone 00: Permaculture for the Inner Landscape (No Land Required)
Zone 00: Permaculture for the Inner Landscape (No Land Required)
 Sam Bankman-Fried files for new trial over FTX fraud charges
Sam Bankman-Fried files for new trial over FTX fraud charges
 Big Tariff Refunds Are Coming. How Much and How Soon?
Big Tariff Refunds Are Coming. How Much and How Soon?
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Sodium ion batteries closer to commercialization
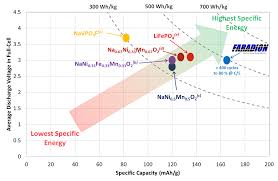
Even though sodium-ion batteries would be physically heavier than lithium-ion technology, researchers have been investigating sodium-ion batteries because they could store energy for large solar and wind power facilities at lower cost.
The problem is that sodium ions stick to the hard carbon end of a battery, called an anode, during the initial charging cycles and not travel over to the cathode end. The ions build up into a structure called a "solid electrolyte interface."
"Normally the solid electrolyte interface is good because it protects carbon particles from a battery's acidic electrolyte, where electricity is conducted," Pol said. "But too much of the interface consumes the sodium ions that we need for charging the battery."

 Iran & Epstein Fallout
Iran & Epstein Fallout


