
Breaking News
 Boots on the Ground...The news is getting worse so keep prepping.
Boots on the Ground...The news is getting worse so keep prepping.
 O'Keefe Media Group: Secret Service Agent Assigned to Vance Leaks Sensitive Information
O'Keefe Media Group: Secret Service Agent Assigned to Vance Leaks Sensitive Information
 Montana Program Makes Youth Offenders Talk with Their Victims and Recidivism Plummets
Montana Program Makes Youth Offenders Talk with Their Victims and Recidivism Plummets
 Gorgeous Bridge Allows for Walking and Biking Between US and Canada Set to Open in 2026
Gorgeous Bridge Allows for Walking and Biking Between US and Canada Set to Open in 2026
Top Tech News
 Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
 World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
 New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
 Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
 Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
 Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
 US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
 Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
 The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
Nobel-winning technology reveals cancer-killing virus locking onto target like a "key in a lock
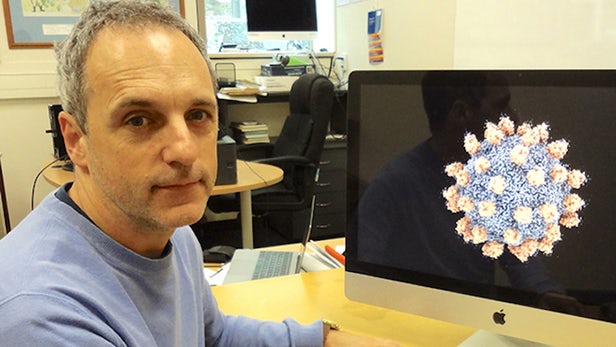
Last year, a cutting edge scientific imaging technology called cryo-electron microscopy earned a Nobel Prize for chemistry, lauded by the committee as ushering in a "revolution in biochemistry." The technique allows scientists to visualize biomolecules in their natural state for the first time ever, and one year on is already opening up some exciting possibilities. Now, scientists have used it to image a high-potential cancer-killing virus in unprecedented detail, allowing them to now ponder how it might be genetically modified to better do the job.
According to the Nobel statement accompanying the announcement last year, cryo-electron microscopy has allowed scientists to "visualise processes they have never previously seen." It relies on a careful freezing method that turns water inside cells into a solid to preserve their cellular structure, along with a modified electron microscope that blasts it with weakened beams for that very same reason.
This, paired with pioneering mathematical algorithms, has already enabled scientists to use cryo-electron microscopy to probe the secrets of poisonous bacteria, polio-fighting plant viruses and the immune-regulating effects of tick saliva. Now, scientists at the University of Otago and the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) are using it to explore the potential for designer viruses that kill off cancer.

 Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this

