
Breaking News
 Wednesday War Room LIVE: Fireworks As AG Pam Bondi Testifies Before Congress On Epstein Files...
Wednesday War Room LIVE: Fireworks As AG Pam Bondi Testifies Before Congress On Epstein Files...
 Trans Suspect Kills Nine, Wounds 25 Before Committing Suicide In HORRIFYING Canadian...
Trans Suspect Kills Nine, Wounds 25 Before Committing Suicide In HORRIFYING Canadian...
 Liberate Education from the State
Liberate Education from the State
 Mark Zuckerberg buys new $150 million Miami mansion after becoming latest tech billionaire...
Mark Zuckerberg buys new $150 million Miami mansion after becoming latest tech billionaire...
Top Tech News
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
 Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
Starlink smasher? China claims world's best high-powered microwave weapon
 Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
Wood scraps turn 'useless' desert sand into concrete
 Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
Let's Do a Detailed Review of Zorin -- Is This Good for Ex-Windows Users?
 The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
The World's First Sodium-Ion Battery EV Is A Winter Range Monster
 China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
China's CATL 5C Battery Breakthrough will Make Most Combustion Engine Vehicles OBSOLETE
Watch tiny robots swim through an eyeball to deliver medicine
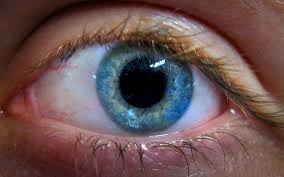
Now, researchers have developed a tiny, rotini-shaped spiral that could one day be deployed in the thousands for targeted drug delivery.
Current treatments for eye diseases such as glaucoma or diabetic macular edema are delivered through direct injection or eyedrops. Those methods are effective but imprecise, often blanketing the entire eye in medication.
So scientists used nanoscale 3D printing to create spiral-shaped robots small enough to pass through the dense jelly known as the vitreous humor that makes up most of the eyeball. The researchers added a slippery coating and magnetic materials so they could propel the microbots through the eye using a magnetic field.
The scientists then collected pig eyes from a slaughterhouse, injected a solution containing about 10,000 bots into each eye, and then placed them in a magnetic field, which they used to propel the bots to the retina at the back of the eye. Imaging showed the swarm successfully reached the retina in less than 30 minutes, about 10 times faster than letting similar-size particles diffuse through the eye, the researchers reported last week in Science Advances.



