
Breaking News
 US Deploys F-22 Fighter Jets to Southern Israel as Massive Military Buildup Continues
US Deploys F-22 Fighter Jets to Southern Israel as Massive Military Buildup Continues
 Elon Musk 'Legacy media lies relentlessly' from clip: It is the media that is racist'
Elon Musk 'Legacy media lies relentlessly' from clip: It is the media that is racist'
 Zohran Mamdani forces cops to pray to Allah (2nd clip) – He and AOC announce free health care...
Zohran Mamdani forces cops to pray to Allah (2nd clip) – He and AOC announce free health care...
 Why Can't We Thrive Like 1905?
Why Can't We Thrive Like 1905?
Top Tech News
 New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
New Spray-on Powder Instantly Seals Life-Threatening Wounds in Battle or During Disasters
 AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
AI-enhanced stethoscope excels at listening to our hearts
 Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
Flame-treated sunscreen keeps the zinc but cuts the smeary white look
 Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
Display hub adds three more screens powered through single USB port
 We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
We Finally Know How Fast The Tesla Semi Will Charge: Very, Very Fast
 Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
Drone-launching underwater drone hitches a ride on ship and sub hulls
 Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
Humanoid Robots Get "Brains" As Dual-Use Fears Mount
 SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
SpaceX Authorized to Increase High Speed Internet Download Speeds 5X Through 2026
 Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
Space AI is the Key to the Technological Singularity
 Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Velocitor X-1 eVTOL could be beating the traffic in just a year
Nanotube film enabling ten times higher energy lithium metal batteries
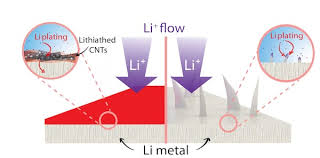
Over time, these tentacle-like dendrites can pierce the battery's electrolyte core and reach the cathode, causing the battery to fail. That problem has mostly stopped the use of lithium metal in commercial applications.
Lithium metal charges much faster and holds about 10 times more energy by volume than the lithium-ion electrodes commonly used today.
The tangled-nanotube film effectively quenched dendrites over 580 charge/discharge cycles of a test battery with a sulfurized-carbon cathode the lab developed in previous experiments. The researchers reported the full lithium metal cells retained 99.8 percent of their coulombic efficiency, the measure of how well electrons move within an electrochemical system.



