
Breaking News
 Boots on the Ground...The news is getting worse so keep prepping.
Boots on the Ground...The news is getting worse so keep prepping.
 O'Keefe Media Group: Secret Service Agent Assigned to Vance Leaks Sensitive Information
O'Keefe Media Group: Secret Service Agent Assigned to Vance Leaks Sensitive Information
 Montana Program Makes Youth Offenders Talk with Their Victims and Recidivism Plummets
Montana Program Makes Youth Offenders Talk with Their Victims and Recidivism Plummets
 Gorgeous Bridge Allows for Walking and Biking Between US and Canada Set to Open in 2026
Gorgeous Bridge Allows for Walking and Biking Between US and Canada Set to Open in 2026
Top Tech News
 Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
 World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
 New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
 Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
 Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
 Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
 US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
 Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
 The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
Highly adhesive hydrogel sticks to the task of tissue regeneration
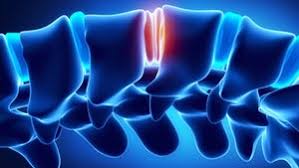
Scientists in Switzerland have now developed a new form of the material they say has unparalleled adhesive properties, a characteristic that could prove particularly useful in trying to repair cartilage and meniscus.
Unlike some other tissues in the human body, cartilage and meniscus have a negligible supply of blood, or none at all, and therefore won't regenerate on their own once damaged. Scientists have already looked to offer a helping hand by injecting hydrogels packed with different drugs into the damaged areas, but these tend to wash away due to the natural machinations of the human body and the flow of its fluids.
In a new study, scientists at Switzerland's École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne describe a new kind of material they think can stick to the task. Their hydrogel is almost 90 percent water and includes of a web of cross-linked polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate together with cross-linked alginate, reinforced with nanofibrillated cellulose.
The resulting structure is claimed to be 10 times more adhesive than commercially available bioadhesives, and due to its high water content, bears a strong similarity to the natural tissues it is supposed to heal. But most importantly, it remains highly adhesive over time because the uniquely layered material absorbs the mechanical stresses that would otherwise wash it away.

 Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this

