
Breaking News
 Boots on the Ground...The news is getting worse so keep prepping.
Boots on the Ground...The news is getting worse so keep prepping.
 O'Keefe Media Group: Secret Service Agent Assigned to Vance Leaks Sensitive Information
O'Keefe Media Group: Secret Service Agent Assigned to Vance Leaks Sensitive Information
 Montana Program Makes Youth Offenders Talk with Their Victims and Recidivism Plummets
Montana Program Makes Youth Offenders Talk with Their Victims and Recidivism Plummets
 Gorgeous Bridge Allows for Walking and Biking Between US and Canada Set to Open in 2026
Gorgeous Bridge Allows for Walking and Biking Between US and Canada Set to Open in 2026
Top Tech News
 Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
Superheat Unveils the H1: A Revolutionary Bitcoin-Mining Water Heater at CES 2026
 World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
World's most powerful hypergravity machine is 1,900X stronger than Earth
 New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
New battery idea gets lots of power out of unusual sulfur chemistry
 Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
Anti-Aging Drug Regrows Knee Cartilage in Major Breakthrough That Could End Knee Replacements
 Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
Scientists say recent advances in Quantum Entanglement...
 Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
Solid-State Batteries Are In 'Trailblazer' Mode. What's Holding Them Up?
 US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
US Farmers Began Using Chemical Fertilizer After WW2. Comfrey Is a Natural Super Fertilizer
 Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
Kawasaki's four-legged robot-horse vehicle is going into production
 The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
The First Production All-Solid-State Battery Is Here, And It Promises 5-Minute Charging
Chemotherapy revealed as toxic poison for every living cell in the human body: Mitochondrial ...
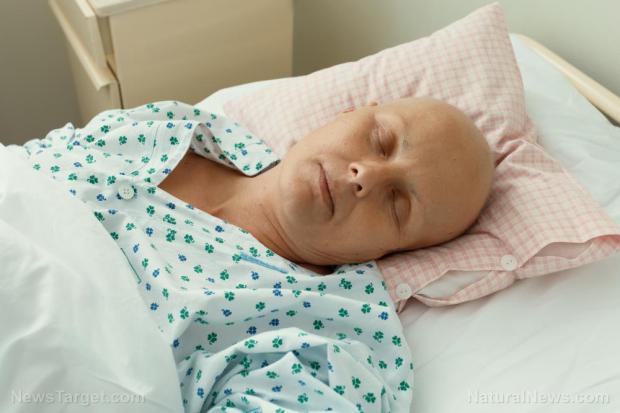
(Natural News) Chemotherapy is not medicine; it is not a therapy at all. A new study published in the American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology lambastes chemotherapy for causing mitochondrial dysfunction in patients' muscles. This is not some simple side effect. This is a direct debilitating effect inflicted on patients, a condition that causes fatigue, weakness, oxidative stress, and muscle wasting in patients. The research, conducted at the University of Vermont, finds that breast cancer patients are harmed by the chemotherapy drugs doxorubicin and paclitaxel. These are the so-called medications that are commonly used post-surgery in breast cancer patients.
The mitochondria are the energy center of the cells. Cancer treatment should maximize the energy production of cells, not restrict it. Maximizing mitochondrial energy production is one of the keys for a healthy cancer recovery. Breast cancer drugs are literally creating the conditions for future cancers to develop and take hold. (Related: Chemotherapy found to increase the number of tumor cells circulating in the blood, spreading it to previously unaffected areas.)
Chemotherapy drugs destroy mitochondria of healthy cells, initiating chronic disease conditions
To get a better understanding, the University of Vermont research team compared muscle fibers from women undergoing chemotherapy for breast cancer post tumor removal. Compared to a healthy control group, these women experienced pronounced muscle loss, indicated by a lower cross sectional area of muscle fibers. Next, the researchers applied chemotherapy drugs to mouse muscle cells and studied their mitochondria. The mitochondria were significantly reduced in number and oxidative stress was discovered along with atrophy. The researchers found that doxorubicin and paclitaxel inflict severe oxidative stress which damages cells, restricts mitochondrial energy production, speeds up cell death, and initiates the conditions for chronic diseases.

 Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this
Storage doesn't get much cheaper than this

